Dispersion from Diffuse Reflectors and its Effect of Terahertz Wireless Communication Performance
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2021
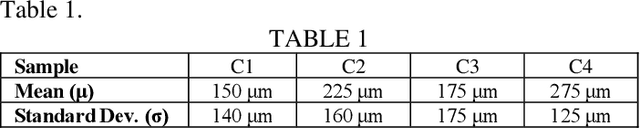

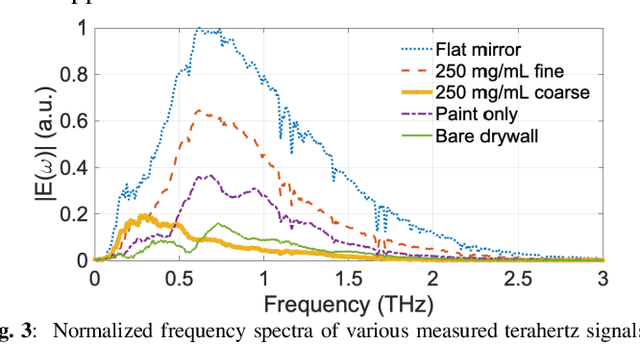
This work investigates the temporal dispersion of a wireless terahertz communication signal caused by reflection from a rough (diffuse) surface, and its subsequent impact on symbol error rate versus data rate. Broadband measurements of diffuse reflectors using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy were used to establish and validate a scattering model that uses stochastic methods to describe the effects of surface roughness on the phase and amplitude of a reflected terahertz signal, expressed as a communication channel transfer function. The modeled channel was used to simulate a quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK)- modulated wireless communication link to determine the relationships between symbol error rate and data rate as a function of surface roughness. The simulations reveal that surface roughness from wall texturing results in group delay dispersion that limits achievable data rate with low errors. A distinct dispersion limit in surface roughness is discovered beyond which unacceptable numbers of symbol errors begin to accrue for a given data rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge