Discovery of structure-property relations for molecules via hypothesis-driven active learning over the chemical space
Paper and Code
Jan 06, 2023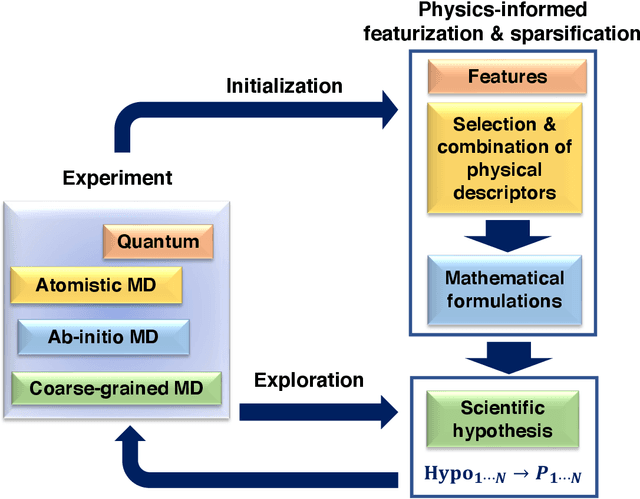
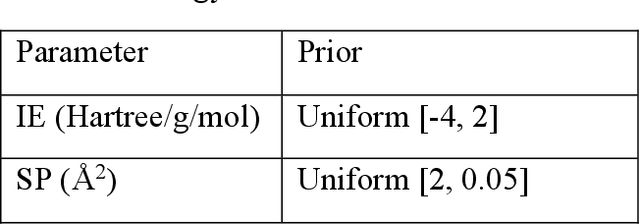

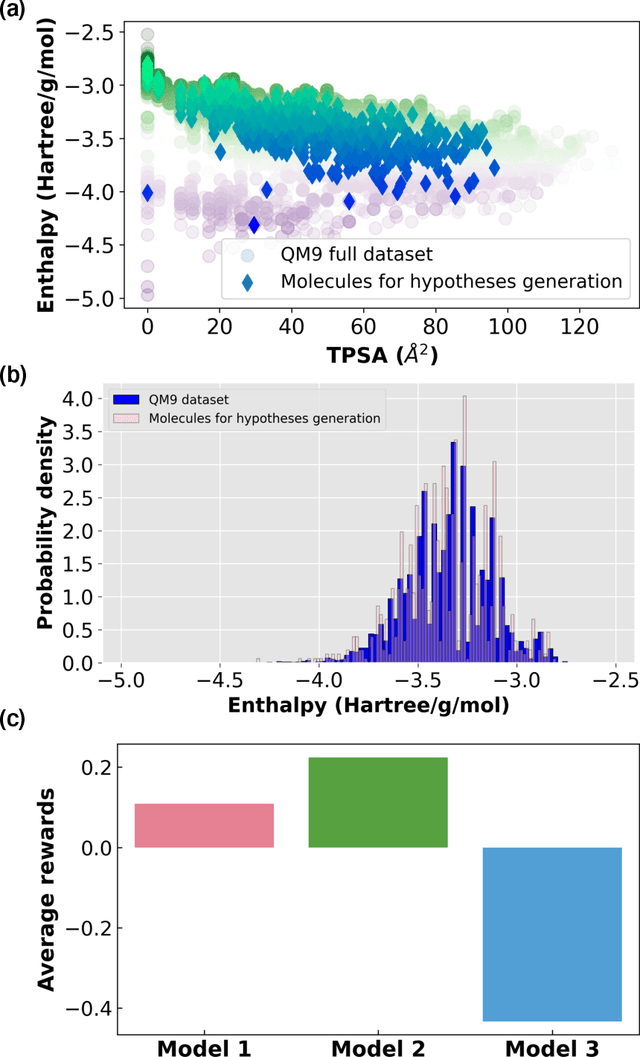
Discovery of the molecular candidates for applications in drug targets, biomolecular systems, catalysts, photovoltaics, organic electronics, and batteries, necessitates development of machine learning algorithms capable of rapid exploration of the chemical spaces targeting the desired functionalities. Here we introduce a novel approach for the active learning over the chemical spaces based on hypothesis learning. We construct the hypotheses on the possible relationships between structures and functionalities of interest based on a small subset of data and introduce them as (probabilistic) mean functions for the Gaussian process. This approach combines the elements from the symbolic regression methods such as SISSO and active learning into a single framework. Here, we demonstrate it for the QM9 dataset, but it can be applied more broadly to datasets from both domains of molecular and solid-state materials sciences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge