Differentially Private M-band Wavelet-Based Mechanisms in Machine Learning Environments
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2020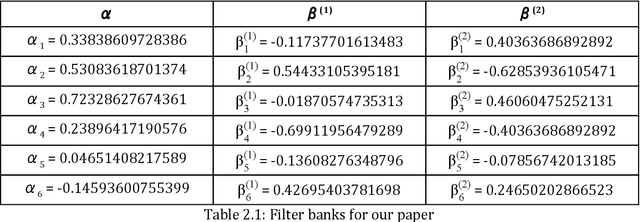

In the post-industrial world, data science and analytics have gained paramount importance regarding digital data privacy. Improper methods of establishing privacy for accessible datasets can compromise large amounts of user data even if the adversary has a small amount of preliminary knowledge of a user. Many researchers have been developing high-level privacy-preserving mechanisms that also retain the statistical integrity of the data to apply to machine learning. Recent developments of differential privacy, such as the Laplace and Privelet mechanisms, drastically decrease the probability that an adversary can distinguish the elements in a data set and thus extract user information. In this paper, we develop three privacy-preserving mechanisms with the discrete M-band wavelet transform that embed noise into data. The first two methods (LS and LS+) add noise through a Laplace-Sigmoid distribution that multiplies Laplace-distributed values with the sigmoid function, and the third method utilizes pseudo-quantum steganography to embed noise into the data. We then show that our mechanisms successfully retain both differential privacy and learnability through statistical analysis in various machine learning environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge