Detection of Malaria Vector Breeding Habitats using Topographic Models
Paper and Code
Nov 27, 2020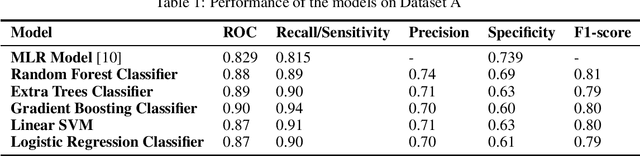
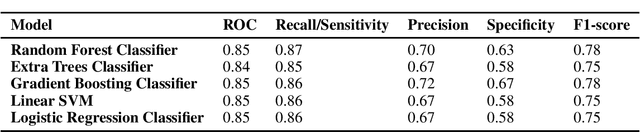
Treatment of stagnant water bodies that act as a breeding site for malarial vectors is a fundamental step in most malaria elimination campaigns. However, identification of such water bodies over large areas is expensive, labour-intensive and time-consuming and hence, challenging in countries with limited resources. Practical models that can efficiently locate water bodies can target the limited resources by greatly reducing the area that needs to be scanned by the field workers. To this end, we propose a practical topographic model based on easily available, global, high-resolution DEM data to predict locations of potential vector-breeding water sites. We surveyed the Obuasi region of Ghana to assess the impact of various topographic features on different types of water bodies and uncover the features that significantly influence the formation of aquatic habitats. We further evaluate the effectiveness of multiple models. Our best model significantly outperforms earlier attempts that employ topographic variables for detection of small water sites, even the ones that utilize additional satellite imagery data and demonstrates robustness across different settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge