Detecting Fake Points of Interest from Location Data
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2021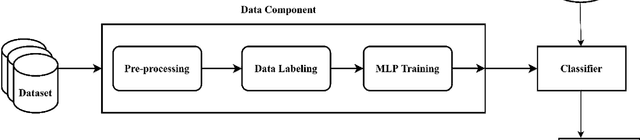
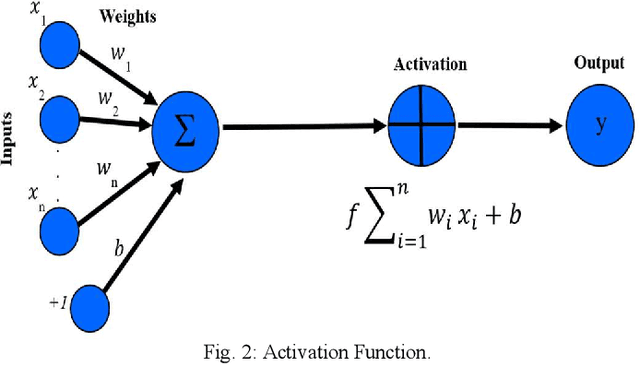
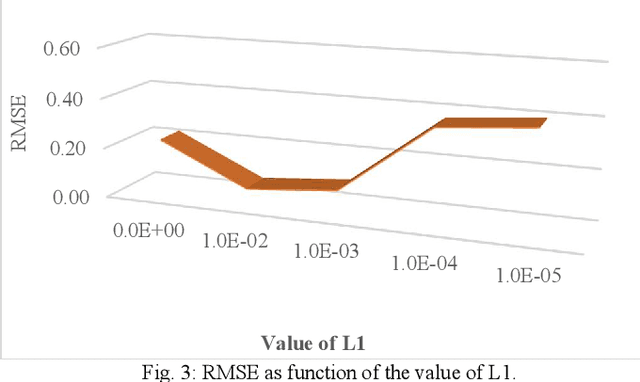
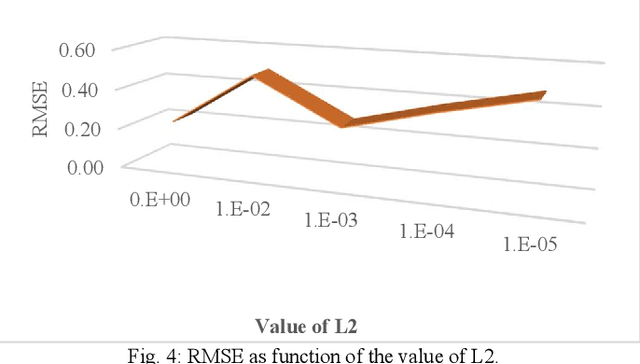
The pervasiveness of GPS-enabled mobile devices and the widespread use of location-based services have resulted in the generation of massive amounts of geo-tagged data. In recent times, the data analysis now has access to more sources, including reviews, news, and images, which also raises questions about the reliability of Point-of-Interest (POI) data sources. While previous research attempted to detect fake POI data through various security mechanisms, the current work attempts to capture the fake POI data in a much simpler way. The proposed work is focused on supervised learning methods and their capability to find hidden patterns in location-based data. The ground truth labels are obtained through real-world data, and the fake data is generated using an API, so we get a dataset with both the real and fake labels on the location data. The objective is to predict the truth about a POI using the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) method. In the proposed work, MLP based on data classification technique is used to classify location data accurately. The proposed method is compared with traditional classification and robust and recent deep neural methods. The results show that the proposed method is better than the baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge