Detecting Compromised Implicit Association Test Results Using Supervised Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 03, 2019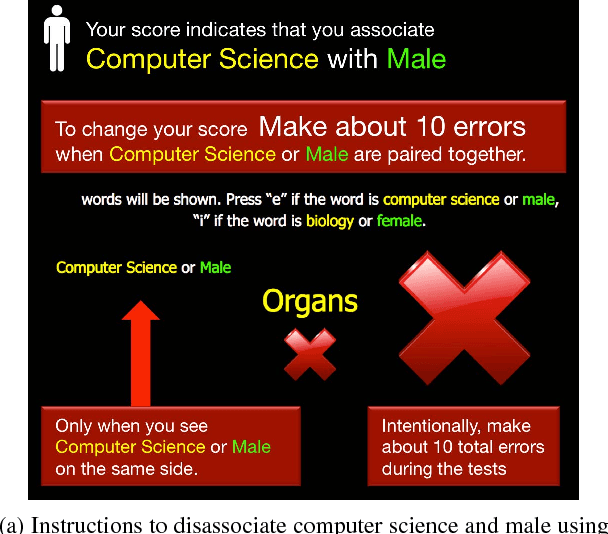
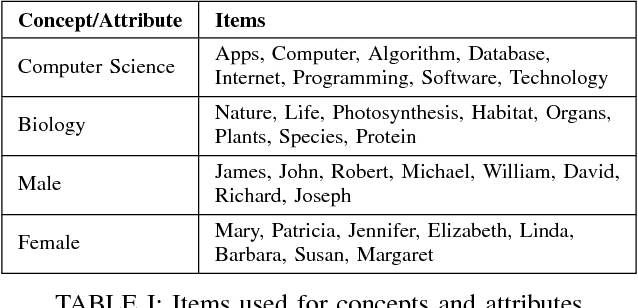

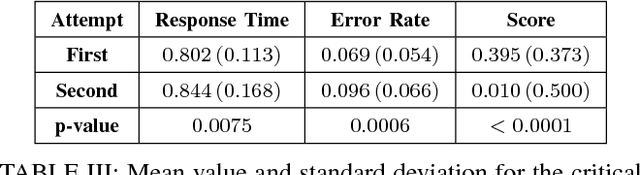
An implicit association test is a human psychological test used to measure subconscious associations. While widely recognized by psychologists as an effective tool in measuring attitudes and biases, the validity of the results can be compromised if a subject does not follow the instructions or attempts to manipulate the outcome. Compared to previous work, we collect training data using a more generalized methodology. We train a variety of different classifiers to identify a participant's first attempt versus a second possibly compromised attempt. To compromise the second attempt, participants are shown their score and are instructed to change it using one of five randomly selected deception methods. Compared to previous work, our methodology demonstrates a more robust and practical framework for accurately identifying a wide variety of deception techniques applicable to the IAT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge