Detecting Anti-Semitic Hate Speech using Transformer-based Large Language Models
Paper and Code
May 06, 2024

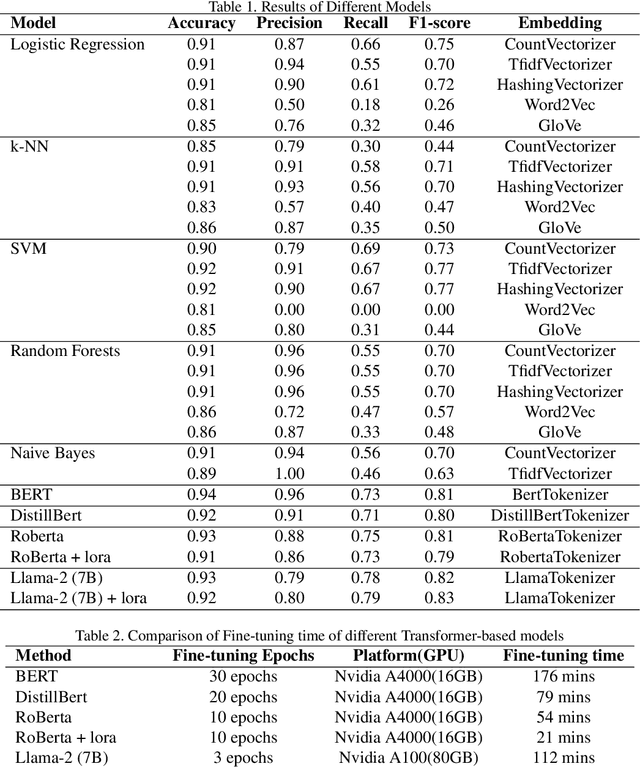
Academic researchers and social media entities grappling with the identification of hate speech face significant challenges, primarily due to the vast scale of data and the dynamic nature of hate speech. Given the ethical and practical limitations of large predictive models like ChatGPT in directly addressing such sensitive issues, our research has explored alternative advanced transformer-based and generative AI technologies since 2019. Specifically, we developed a new data labeling technique and established a proof of concept targeting anti-Semitic hate speech, utilizing a variety of transformer models such as BERT (arXiv:1810.04805), DistillBERT (arXiv:1910.01108), RoBERTa (arXiv:1907.11692), and LLaMA-2 (arXiv:2307.09288), complemented by the LoRA fine-tuning approach (arXiv:2106.09685). This paper delineates and evaluates the comparative efficacy of these cutting-edge methods in tackling the intricacies of hate speech detection, highlighting the need for responsible and carefully managed AI applications within sensitive contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge