Detecting Adversarial Examples in Batches -- a geometrical approach
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2022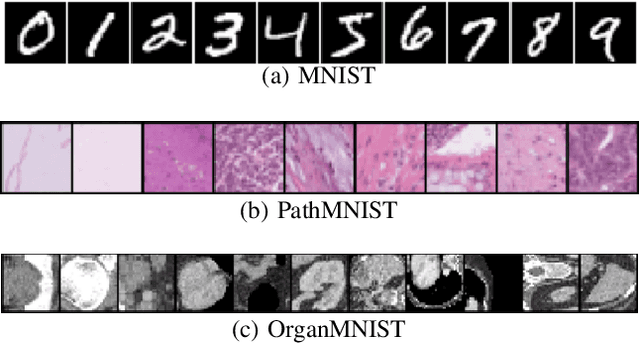
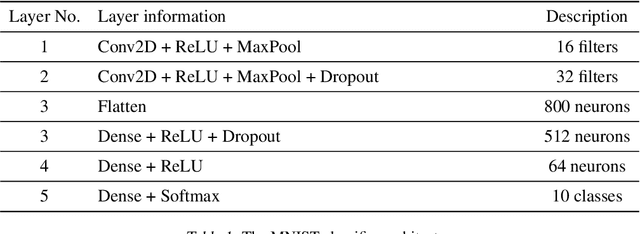
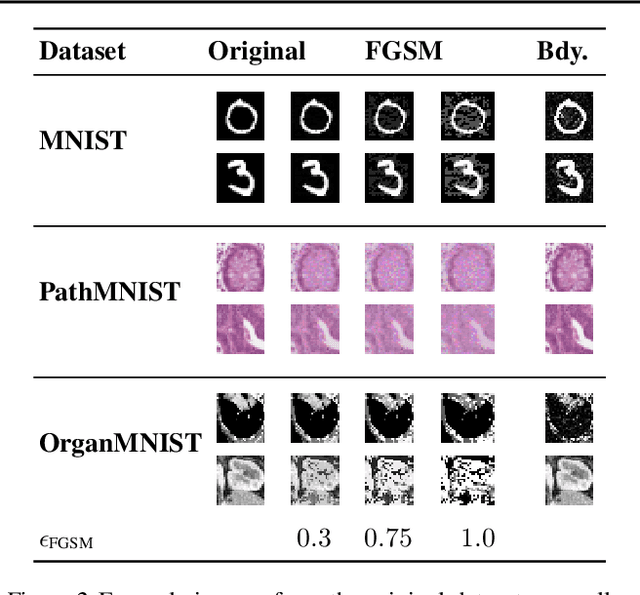

Many deep learning methods have successfully solved complex tasks in computer vision and speech recognition applications. Nonetheless, the robustness of these models has been found to be vulnerable to perturbed inputs or adversarial examples, which are imperceptible to the human eye, but lead the model to erroneous output decisions. In this study, we adapt and introduce two geometric metrics, density and coverage, and evaluate their use in detecting adversarial samples in batches of unseen data. We empirically study these metrics using MNIST and two real-world biomedical datasets from MedMNIST, subjected to two different adversarial attacks. Our experiments show promising results for both metrics to detect adversarial examples. We believe that his work can lay the ground for further study on these metrics' use in deployed machine learning systems to monitor for possible attacks by adversarial examples or related pathologies such as dataset shift.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge