Demystifying Swarm Learning: A New Paradigm of Blockchain-based Decentralized Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 17, 2022
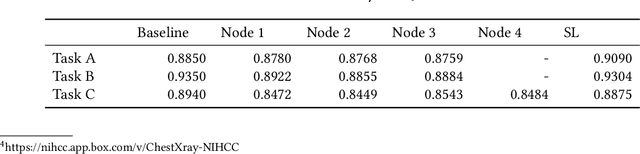

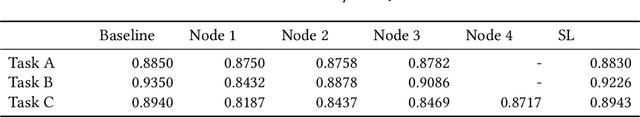
Federated learning (FL) is an emerging promising privacy-preserving machine learning paradigm and has raised more and more attention from researchers and developers. FL keeps users' private data on devices and exchanges the gradients of local models to cooperatively train a shared Deep Learning (DL) model on central custodians. However, the security and fault tolerance of FL have been increasingly discussed, because its central custodian mechanism or star-shaped architecture can be vulnerable to malicious attacks or software failures. To address these problems, Swarm Learning (SL) introduces a permissioned blockchain to securely onboard members and dynamically elect the leader, which allows performing DL in an extremely decentralized manner. Compared with tremendous attention to SL, there are few empirical studies on SL or blockchain-based decentralized FL, which provide comprehensive knowledge of best practices and precautions of deploying SL in real-world scenarios. Therefore, we conduct the first comprehensive study of SL to date, to fill the knowledge gap between SL deployment and developers, as far as we are concerned. In this paper, we conduct various experiments on 3 public datasets of 5 research questions, present interesting findings, quantitatively analyze the reasons behind these findings, and provide developers and researchers with practical suggestions. The findings have evidenced that SL is supposed to be suitable for most application scenarios, no matter whether the dataset is balanced, polluted, or biased over irrelevant features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge