Demystifying 5G NR Downlink Synchronization for Tactical Networks
Paper and Code
May 21, 2024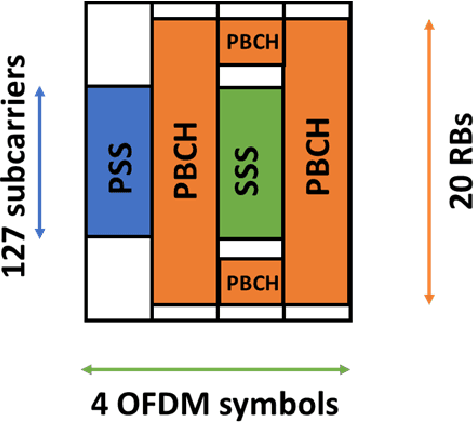
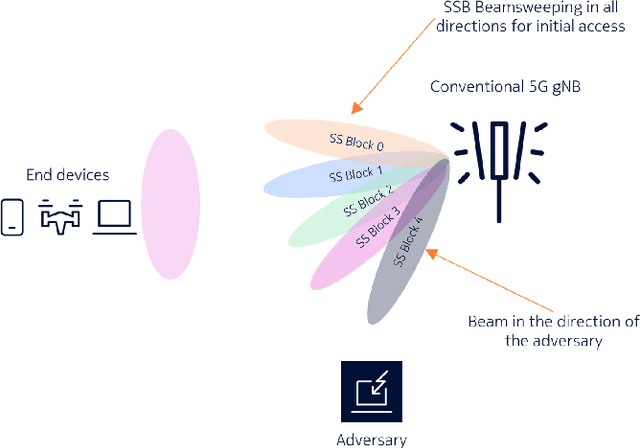
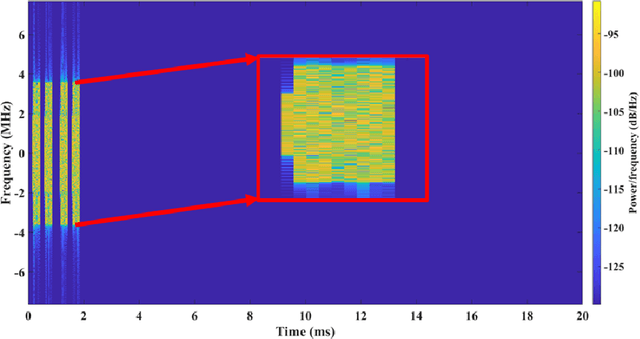
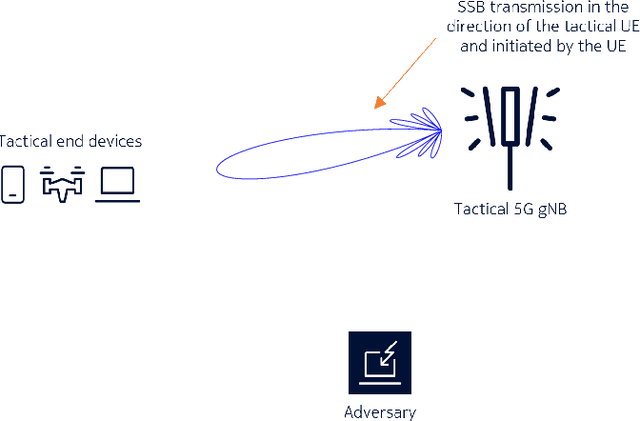
5G NR is touted to be an attractive candidate for tactical networks owing to its versatility, scalability, and low cost. However, tactical networks need to be stealthy, where an adversary is not able to detect or intercept the tactical communication. In this paper, we investigate the stealthiness of 5G NR by looking at the probability with which an adversary that monitors the downlink synchronization signals can detect the presence of the network. We simulate a single-cell single-eavesdropper scenario and evaluate the probability with which the eavesdropper can detect the synchronization signal block when using either a correlator or an energy detector. We show that this probability is close to $ 100 $% suggesting that 5G out-of-the-box is not suitable for a tactical network. We then propose methods that lower this value without affecting the performance of a legitimate tactical UE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge