DeltaBound Attack: Efficient decision-based attack in low queries regime
Paper and Code
Oct 01, 2022
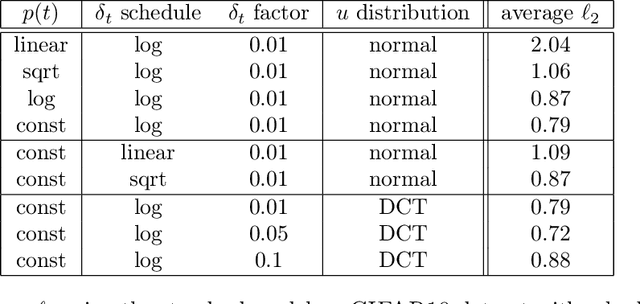
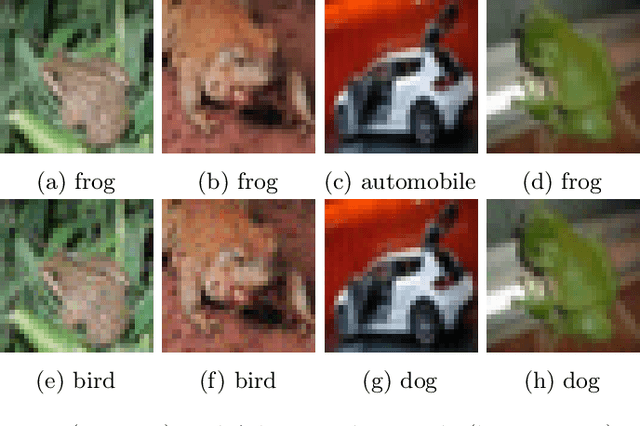
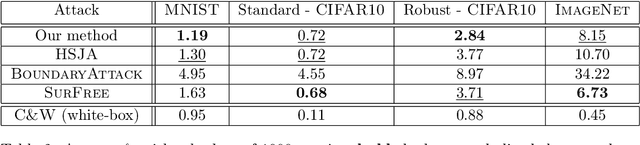
Deep neural networks and other machine learning systems, despite being extremely powerful and able to make predictions with high accuracy, are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. We proposed the DeltaBound attack: a novel, powerful attack in the hard-label setting with $\ell_2$ norm bounded perturbations. In this scenario, the attacker has only access to the top-1 predicted label of the model and can be therefore applied to real-world settings such as remote API. This is a complex problem since the attacker has very little information about the model. Consequently, most of the other techniques present in the literature require a massive amount of queries for attacking a single example. Oppositely, this work mainly focuses on the evaluation of attack's power in the low queries regime $\leq 1000$ queries) with $\ell_2$ norm in the hard-label settings. We find that the DeltaBound attack performs as well and sometimes better than current state-of-the-art attacks while remaining competitive across different kinds of models. Moreover, we evaluate our method against not only deep neural networks, but also non-deep learning models, such as Gradient Boosting Decision Trees and Multinomial Naive Bayes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge