Delta-ICM: Entropy Modeling with Delta Function for Learned Image Compression
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024


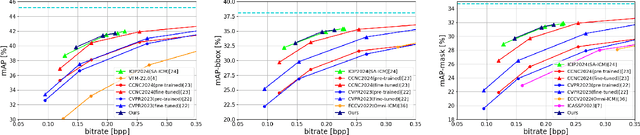
Image Coding for Machines (ICM) is becoming more important as research in computer vision progresses. ICM is a vital research field that pursues the use of images for image recognition models, facilitating efficient image transmission and storage. The demand for recognition models is growing rapidly among the general public, and their performance continues to improve. To meet these needs, exchanging image data between consumer devices and cloud AI using ICM technology could be one possible solution. In ICM, various image compression methods have adopted Learned Image Compression (LIC). LIC includes an entropy model for estimating the bitrate of latent features, and the design of this model significantly affects its performance. Typically, LIC methods assume that the distribution of latent features follows a normal distribution. This assumption is effective for compressing images intended for human vision. However, employing an entropy model based on normal distribution is inefficient in ICM due to the limitation of image parts that require precise decoding. To address this, we propose Delta-ICM, which uses a probability distribution based on a delta function. Assuming the delta distribution as a distribution of latent features reduces the entropy of image portions unnecessary for machines. We compress the remaining portions using an entropy model based on normal distribution, similar to existing methods. Delta-ICM selects between the entropy model based on the delta distribution and the one based on the normal distribution for each latent feature. Our method outperforms existing ICM methods in image compression performance aimed at machines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge