Deep reinforcement learning with automated label extraction from clinical reports accurately classifies 3D MRI brain volumes
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2021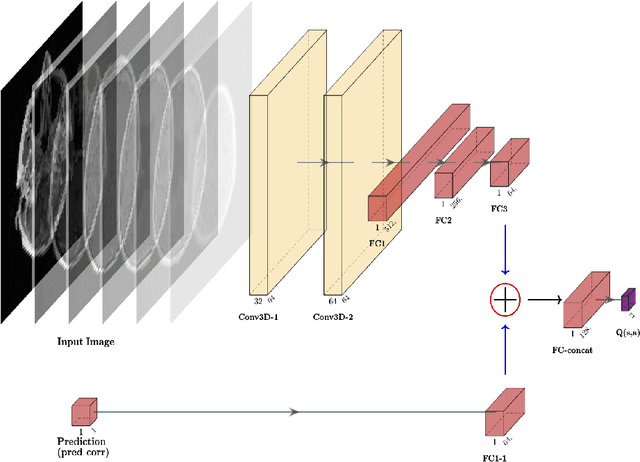
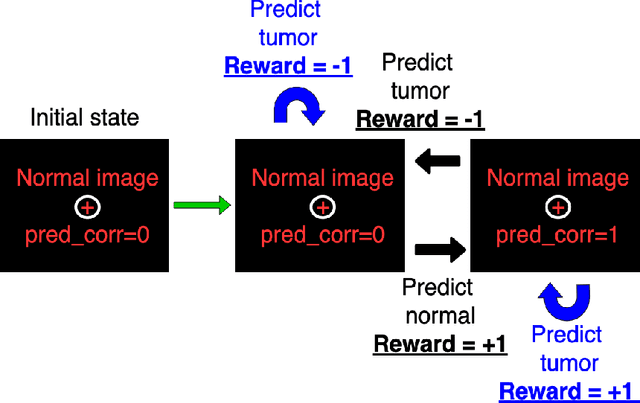
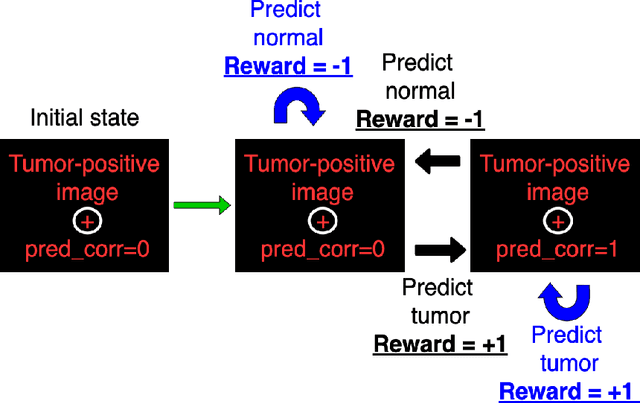
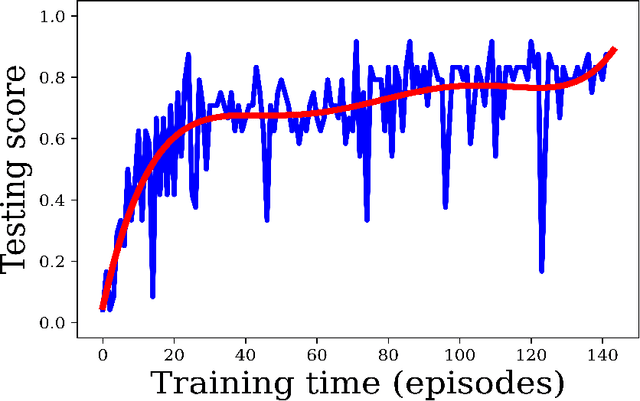
Purpose: Image classification is perhaps the most fundamental task in imaging AI. However, labeling images is time-consuming and tedious. We have recently demonstrated that reinforcement learning (RL) can classify 2D slices of MRI brain images with high accuracy. Here we make two important steps toward speeding image classification: Firstly, we automatically extract class labels from the clinical reports. Secondly, we extend our prior 2D classification work to fully 3D image volumes from our institution. Hence, we proceed as follows: in Part 1, we extract labels from reports automatically using the SBERT natural language processing approach. Then, in Part 2, we use these labels with RL to train a classification Deep-Q Network (DQN) for 3D image volumes. Methods: For Part 1, we trained SBERT with 90 radiology report impressions. We then used the trained SBERT to predict class labels for use in Part 2. In Part 2, we applied multi-step image classification to allow for combined Deep-Q learning using 3D convolutions and TD(0) Q learning. We trained on a set of 90 images. We tested on a separate set of 61 images, again using the classes predicted from patient reports by the trained SBERT in Part 1. For comparison, we also trained and tested a supervised deep learning classification network on the same set of training and testing images using the same labels. Results: Part 1: Upon training with the corpus of radiology reports, the SBERT model had 100% accuracy for both normal and metastasis-containing scans. Part 2: Then, using these labels, whereas the supervised approach quickly overfit the training data and as expected performed poorly on the testing set (66% accuracy, just over random guessing), the reinforcement learning approach achieved an accuracy of 92%. The results were found to be statistically significant, with a p-value of 3.1 x 10^-5.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge