Deep reinforcement learning-based image classification achieves perfect testing set accuracy for MRI brain tumors with a training set of only 30 images
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2021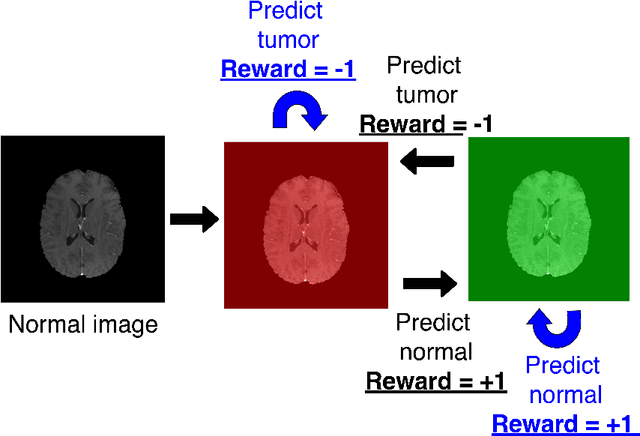
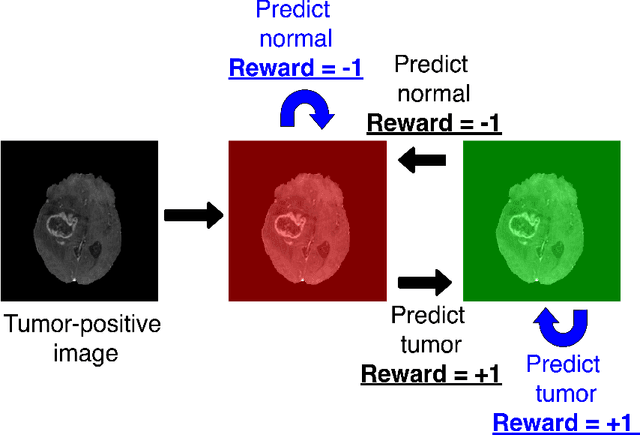
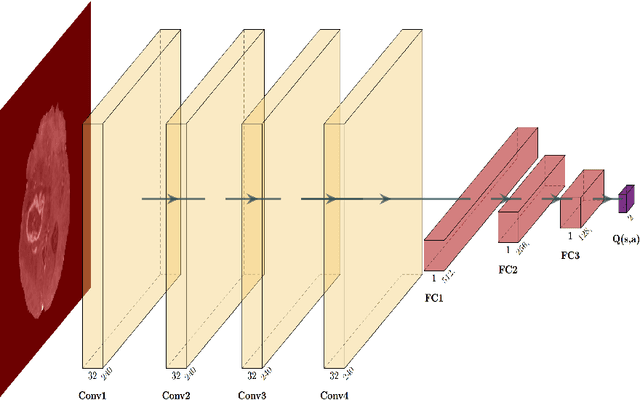
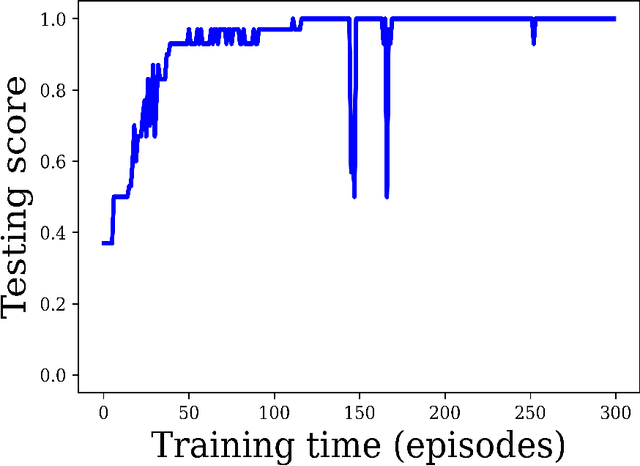
Purpose: Image classification may be the fundamental task in imaging artificial intelligence. We have recently shown that reinforcement learning can achieve high accuracy for lesion localization and segmentation even with minuscule training sets. Here, we introduce reinforcement learning for image classification. In particular, we apply the approach to normal vs. tumor-containing 2D MRI brain images. Materials and Methods: We applied multi-step image classification to allow for combined Deep Q learning and TD(0) Q learning. We trained on a set of 30 images (15 normal and 15 tumor-containing). We tested on a separate set of 30 images (15 normal and 15 tumor-containing). For comparison, we also trained and tested a supervised deep-learning classification network on the same set of training and testing images. Results: Whereas the supervised approach quickly overfit the training data and as expected performed poorly on the testing set (57% accuracy, just over random guessing), the reinforcement learning approach achieved an accuracy of 100%. Conclusion: We have shown a proof-of-principle application of reinforcement learning to the classification of brain tumors. We achieved perfect testing set accuracy with a training set of merely 30 images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge