Deep neural network for optimal retirement consumption in defined contribution pension system
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2020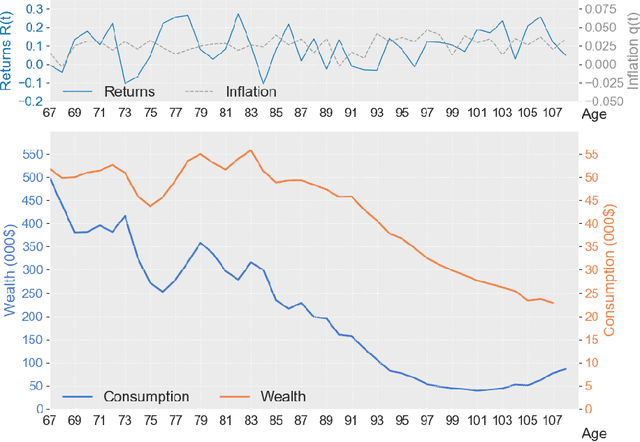
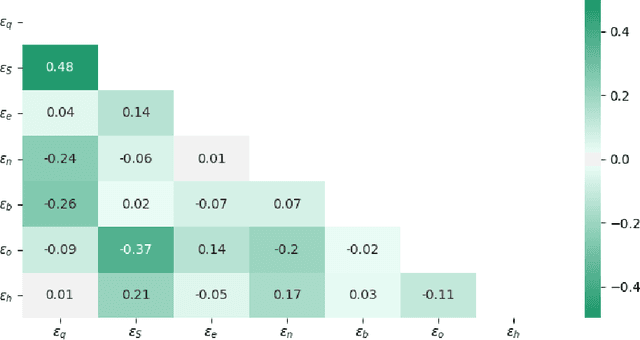
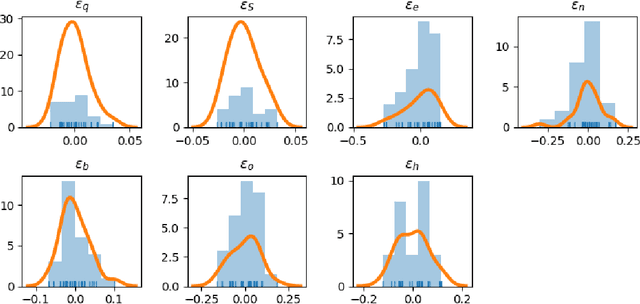

In this paper, we develop a deep neural network approach to solve a lifetime expected mortality-weighted utility-based model for optimal consumption in the decumulation phase of a defined contribution pension system. We formulate this problem as a multi-period finite-horizon stochastic control problem and train a deep neural network policy representing consumption decisions. The optimal consumption policy is determined by personal information about the retiree such as age, wealth, risk aversion and bequest motive, as well as a series of economic and financial variables including inflation rates and asset returns jointly simulated from a proposed seven-factor economic scenario generator calibrated from market data. We use the Australian pension system as an example, with consideration of the government-funded means-tested Age Pension and other practical aspects such as fund management fees. The key findings from our numerical tests are as follows. First, our deep neural network optimal consumption policy, which adapts to changes in market conditions, outperforms deterministic drawdown rules proposed in the literature. Moreover, the out-of-sample outperformance ratios increase as the number of training iterations increases, eventually reaching outperformance on all testing scenarios after less than 10 minutes of training. Second, a sensitivity analysis is performed to reveal how risk aversion and bequest motives change the consumption over a retiree's lifetime under this utility framework. Third, we provide the optimal consumption rate with different starting wealth balances. We observe that optimal consumption rates are not proportional to initial wealth due to the Age Pension payment. Forth, with the same initial wealth balance and utility parameter settings, the optimal consumption level is different between males and females due to gender differences in mortality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge