Deep learning architectures for inference of AC-OPF solutions
Paper and Code
Nov 06, 2020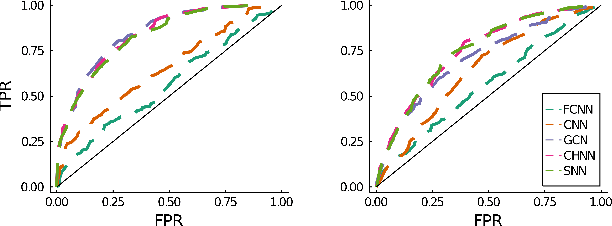
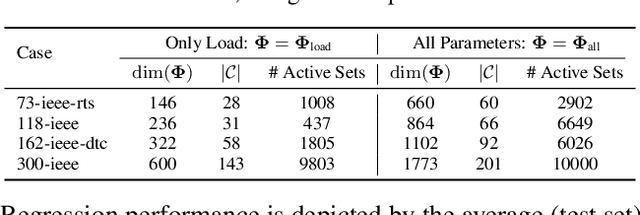
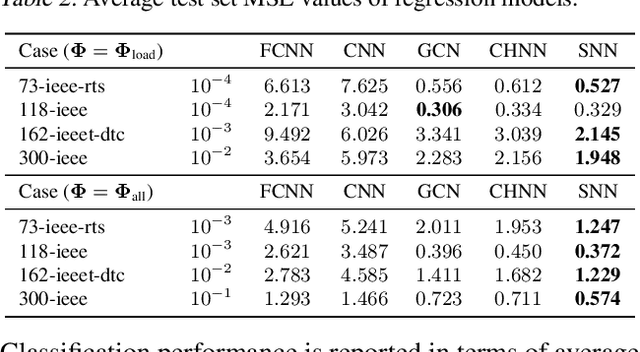
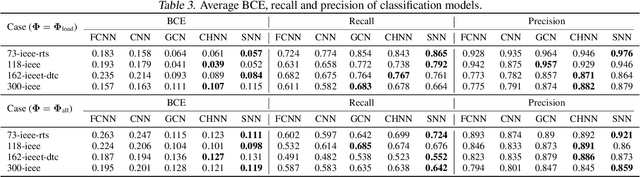
We present a systematic comparison between neural network (NN) architectures for inference of AC-OPF solutions. Using fully connected NNs as a baseline we demonstrate the efficacy of leveraging network topology in models by constructing abstract representations of electrical grids in the graph domain for convolutional and graph NNs. The performance of the NN models is compared for both the direct (as regressors predicting optimal generator set-points) and indirect (as classifiers predicting the active set of constraints) approaches and computational gains for obtaining optimal solutions are also presented.
* 4 pages, 4 tables, 1 figure
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge