Deep Learning Approach for Enhancing Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with LIME Explainable AI Technique
Paper and Code
Nov 21, 2024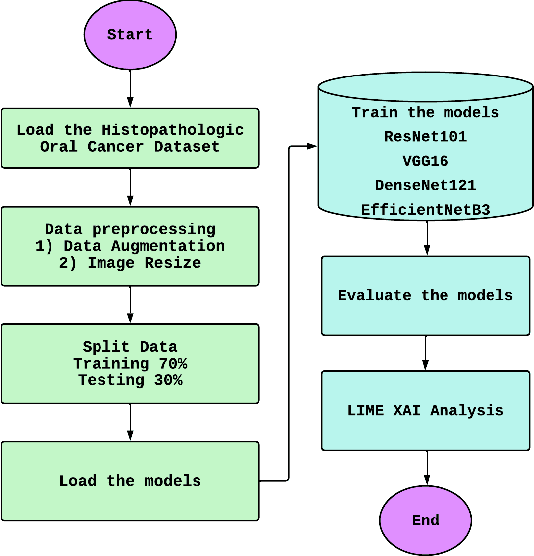
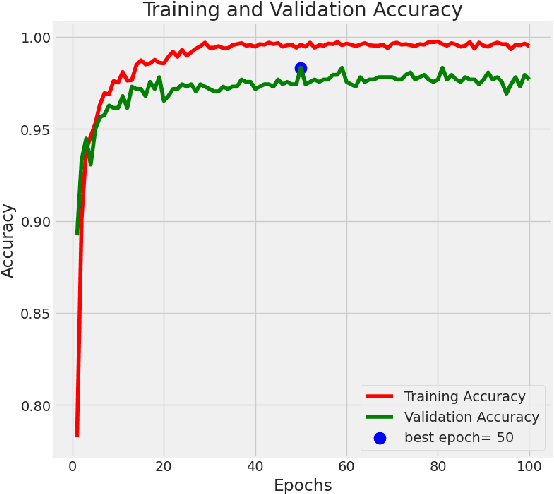
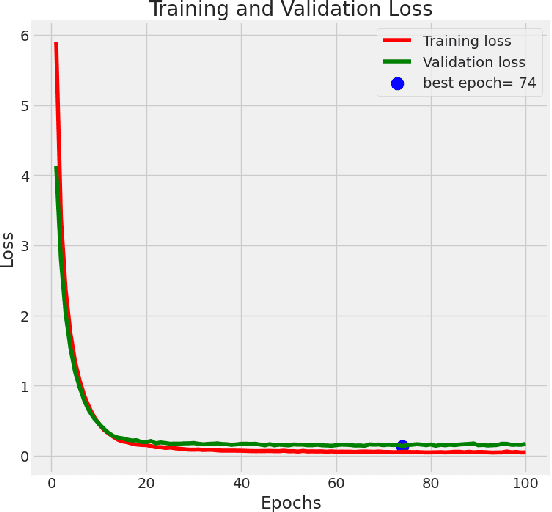
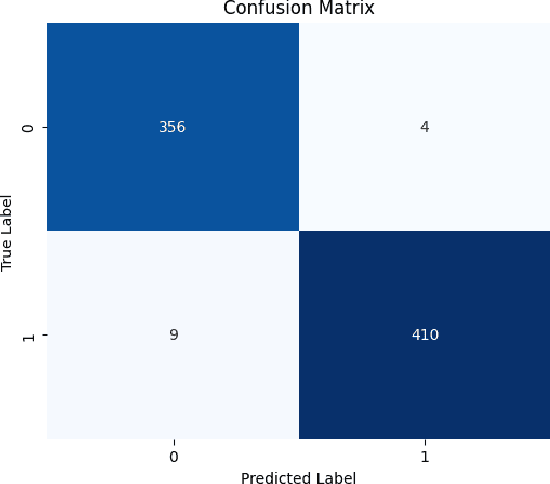
The goal of the present study is to analyze an application of deep learning models in order to augment the diagnostic performance of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) with a longitudinal cohort study using the Histopathological Imaging Database for oral cancer analysis. The dataset consisted of 5192 images (2435 Normal and 2511 OSCC), which were allocated between training, testing, and validation sets with an estimated ratio repartition of about 52% for the OSCC group, and still, our performance measure was validated on a combination set that contains almost equal number of sample in this use case as entire database have been divided into half using stratified splitting technique based again near binary proportion but total distribution was around even. We selected four deep-learning architectures for evaluation in the present study: ResNet101, DenseNet121, VGG16, and EfficientnetB3. EfficientNetB3 was found to be the best, with an accuracy of 98.33% and F1 score (0.9844), and it took remarkably less computing power in comparison with other models. The subsequent one was DenseNet121, with 90.24% accuracy and an F1 score of 90.45%. Moreover, we employed the Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) method to clarify why EfficientNetB3 made certain decisions with its predictions to improve the explainability and trustworthiness of results. This work provides evidence for the possible superior diagnosis in OSCC activated from the EfficientNetB3 model with the explanation of AI techniques such as LIME and paves an important groundwork to build on towards clinical usage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge