Decoding Epileptogenesis in a Reduced State Space
Paper and Code
Jan 25, 2017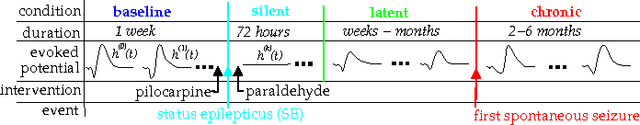
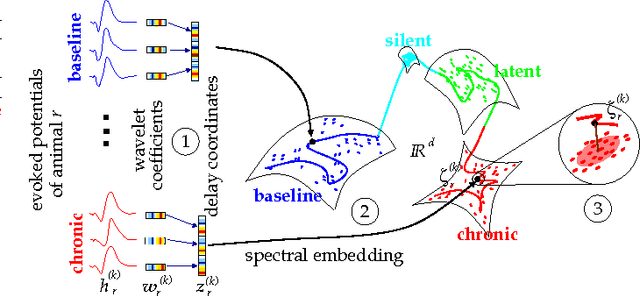
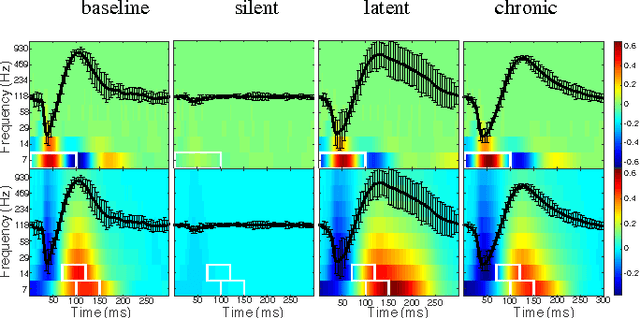
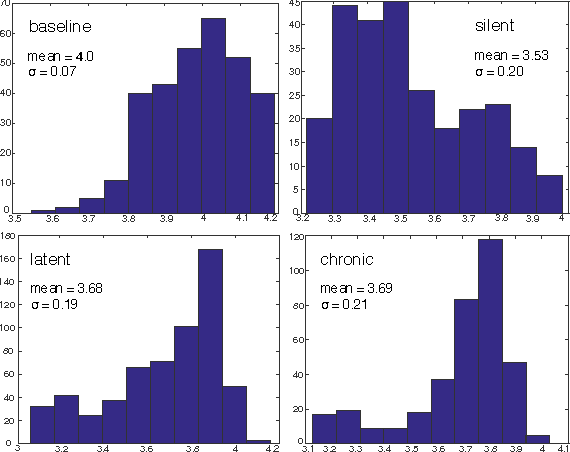
We describe here the recent results of a multidisciplinary effort to design a biomarker that can actively and continuously decode the progressive changes in neuronal organization leading to epilepsy, a process known as epileptogenesis. Using an animal model of acquired epilepsy, wechronically record hippocampal evoked potentials elicited by an auditory stimulus. Using a set of reduced coordinates, our algorithm can identify universal smooth low-dimensional configurations of the auditory evoked potentials that correspond to distinct stages of epileptogenesis. We use a hidden Markov model to learn the dynamics of the evoked potential, as it evolves along these smooth low-dimensional subsets. We provide experimental evidence that the biomarker is able to exploit subtle changes in the evoked potential to reliably decode the stage of epileptogenesis and predict whether an animal will eventually recover from the injury, or develop spontaneous seizures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge