Declipping of Speech Signals Using Frequency Selective Extrapolation
Paper and Code
Apr 07, 2022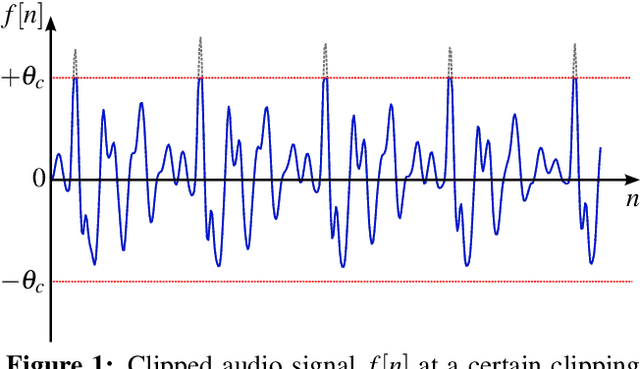

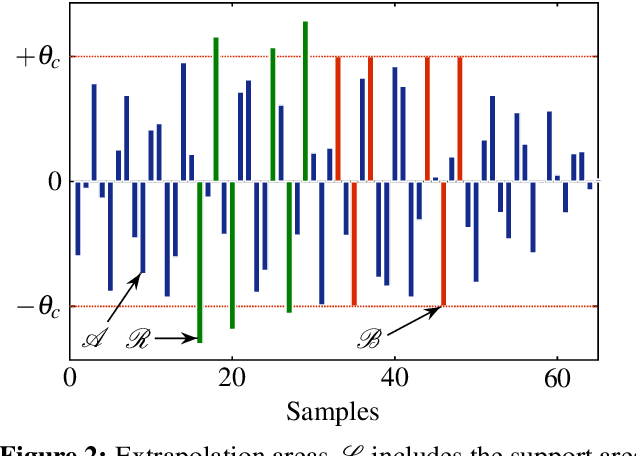
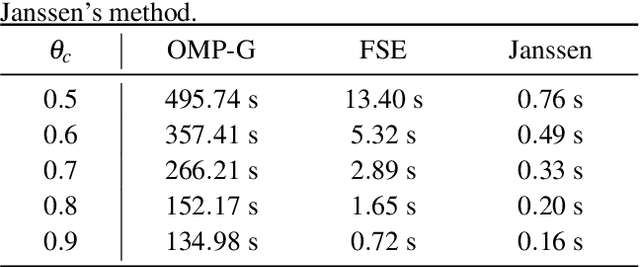
The reconstruction of clipped speech signals is an important task in audio signal processing to achieve an enhanced audio quality for further processing. In this paper, Frequency Selective Extrapolation (FSE), which is commonly used for error concealment or the reconstruction of incomplete image data, is adapted to be able to restore audio signals which are distorted from clipping. For this, FSE generates a model of the signal as an iterative superposition of Fourier basis functions. Clipped samples can then be replaced by estimated samples from the model. The performance of the proposed algorithm is evaluated by using different speech test data sets. Compared to other state-of-the-art declipping algorithms, this leads to a maximum gain in SNR of up to 3:5 dB and an average gain of 1 dB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge