Decision Mamba: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2024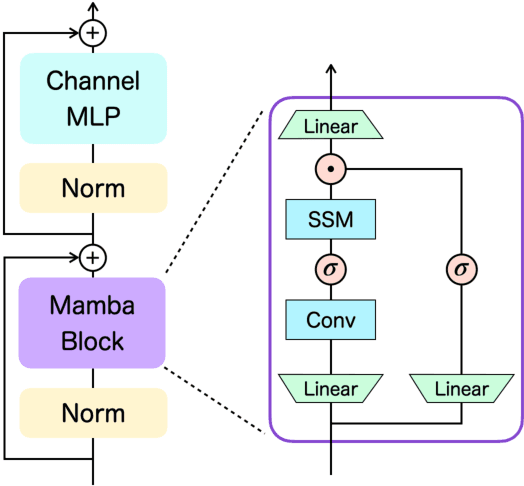
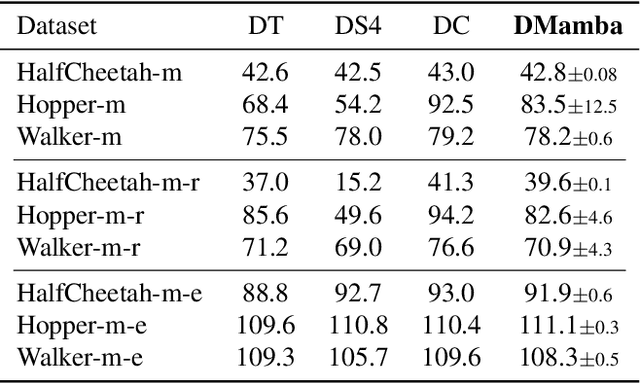
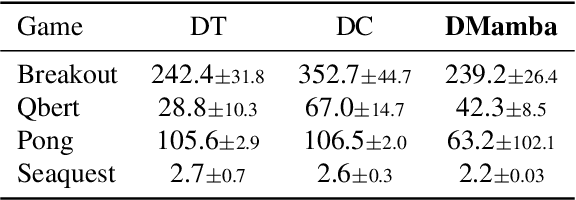
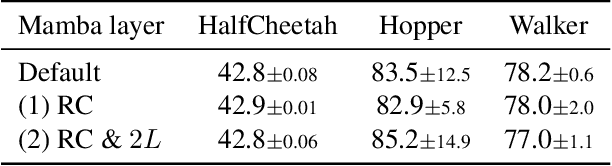
Decision Transformer, a promising approach that applies Transformer architectures to reinforcement learning, relies on causal self-attention to model sequences of states, actions, and rewards. While this method has shown competitive results, this paper investigates the integration of the Mamba framework, known for its advanced capabilities in efficient and effective sequence modeling, into the Decision Transformer architecture, focusing on the potential performance enhancements in sequential decision-making tasks. Our study systematically evaluates this integration by conducting a series of experiments across various decision-making environments, comparing the modified Decision Transformer, Decision Mamba, with its traditional counterpart. This work contributes to the advancement of sequential decision-making models, suggesting that the architecture and training methodology of neural networks can significantly impact their performance in complex tasks, and highlighting the potential of Mamba as a valuable tool for improving the efficacy of Transformer-based models in reinforcement learning scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge