Data Generation in Low Sample Size Setting Using Manifold Sampling and a Geometry-Aware VAE
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2021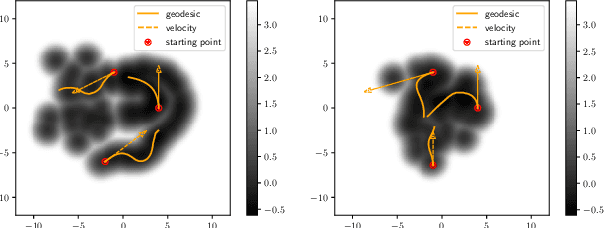
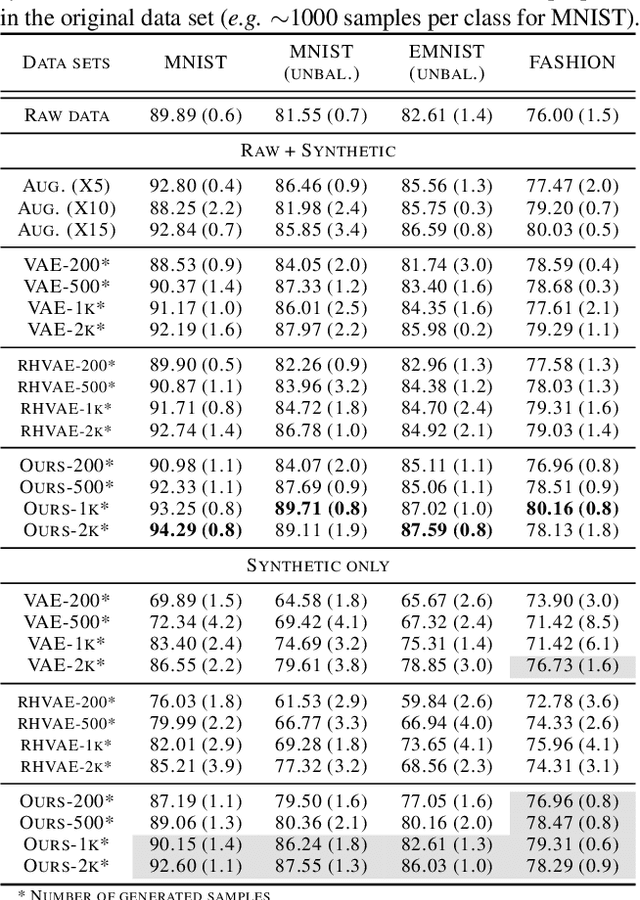
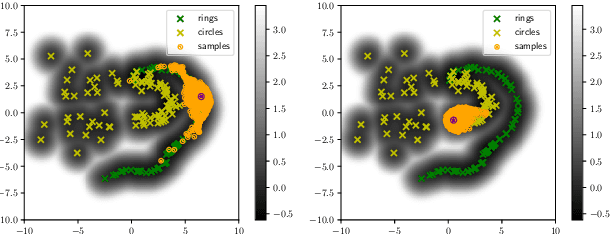
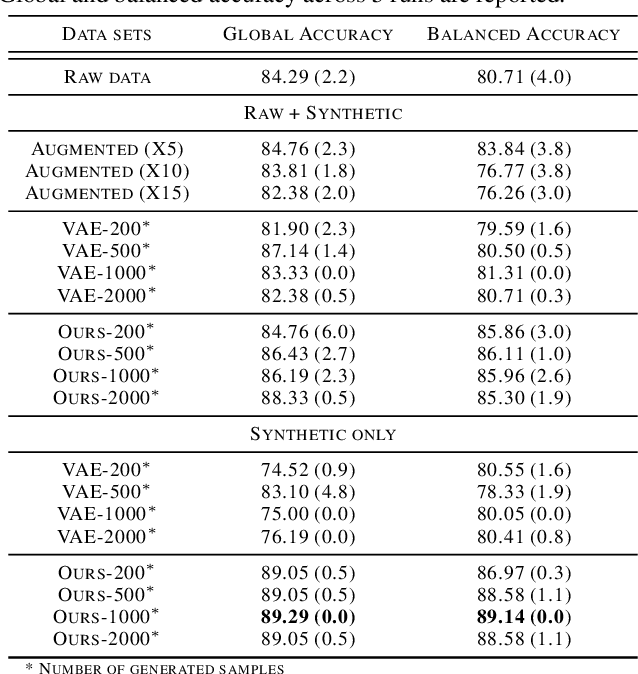
While much efforts have been focused on improving Variational Autoencoders through richer posterior and prior distributions, little interest was shown in amending the way we generate the data. In this paper, we develop two non \emph{prior-dependent} generation procedures based on the geometry of the latent space seen as a Riemannian manifold. The first one consists in sampling along geodesic paths which is a natural way to explore the latent space while the second one consists in sampling from the inverse of the metric volume element which is easier to use in practice. Both methods are then compared to \emph{prior-based} methods on various data sets and appear well suited for a limited data regime. Finally, the latter method is used to perform data augmentation in a small sample size setting and is validated across various standard and \emph{real-life} data sets. In particular, this scheme allows to greatly improve classification results on the OASIS database where balanced accuracy jumps from 80.7% for a classifier trained with the raw data to 89.1% when trained only with the synthetic data generated by our method. Such results were also observed on 4 standard data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge