Data-Driven Graph Switching for Cyber-Resilient Control in Microgrids
Paper and Code
Nov 12, 2024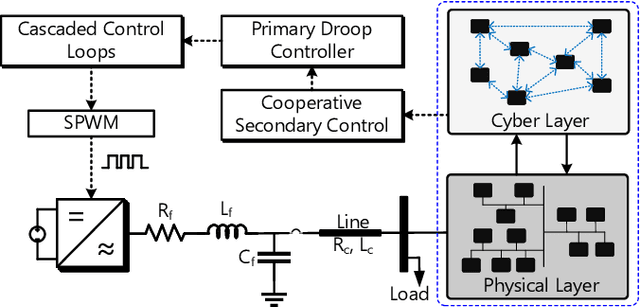
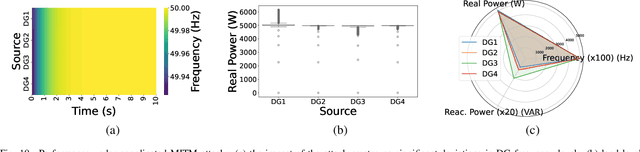
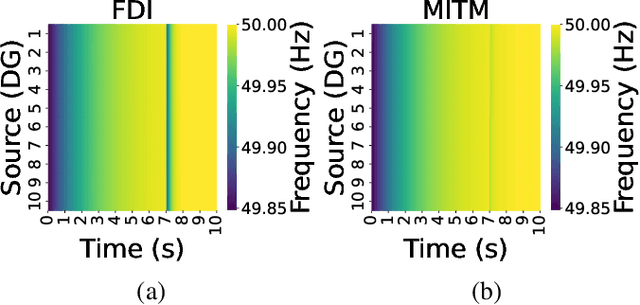
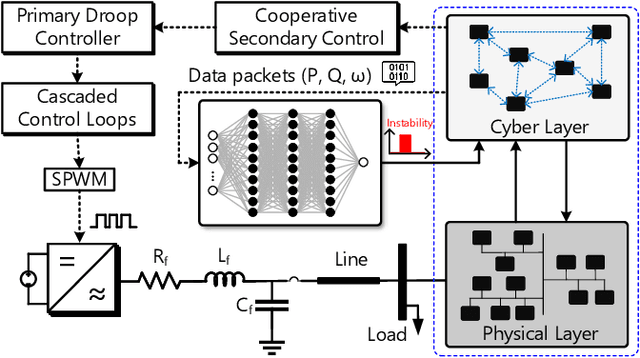
Distributed microgrids are conventionally dependent on communication networks to achieve secondary control objectives. This dependence makes them vulnerable to stealth data integrity attacks (DIAs) where adversaries may perform manipulations via infected transmitters and repeaters to jeopardize stability. This paper presents a physics-guided, supervised Artificial Neural Network (ANN)-based framework that identifies communication-level cyberattacks in microgrids by analyzing whether incoming measurements will cause abnormal behavior of the secondary control layer. If abnormalities are detected, an iteration through possible spanning tree graph topologies that can be used to fulfill secondary control objectives is done. Then, a communication network topology that would not create secondary control abnormalities is identified and enforced for maximum stability. By altering the communication graph topology, the framework eliminates the dependence of the secondary control layer on inputs from compromised cyber devices helping it achieve resilience without instability. Several case studies are provided showcasing the robustness of the framework against False Data Injections and repeater-level Man-in-the-Middle attacks. To understand practical feasibility, robustness is also verified against larger microgrid sizes and in the presence of varying noise levels. Our findings indicate that performance can be affected when attempting scalability in the presence of noise. However, the framework operates robustly in low-noise settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge