Data-driven cortical clustering to provide a family of plausible solutions to M/EEG inverse problem
Paper and Code
Dec 07, 2018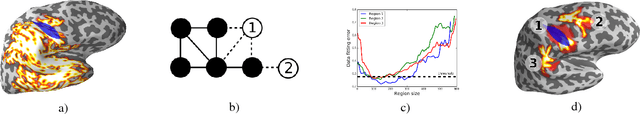
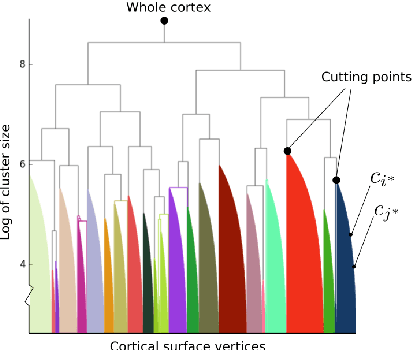
The M/EEG inverse problem is ill-posed. Thus additional hypotheses are needed to constrain the solution space. In this work, we consider that brain activity which generates an M/EEG signal is a connected cortical region. We study the case when only one region is active at once. We show that even in this simple case several configurations can explain the data. As opposed to methods based on convex optimization which are forced to select one possible solution, we propose an approach which is able to find several "good" candidates - regions which are different in term of their sizes and/or positions but fit the data with similar accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge