CSI-Net: Unified Human Body Characterization and Action Recognition
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2018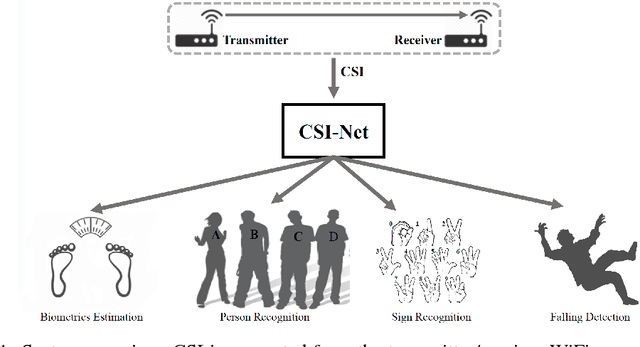
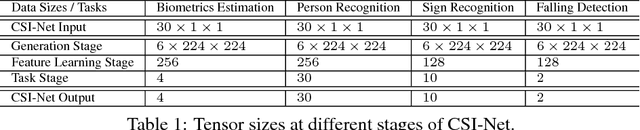
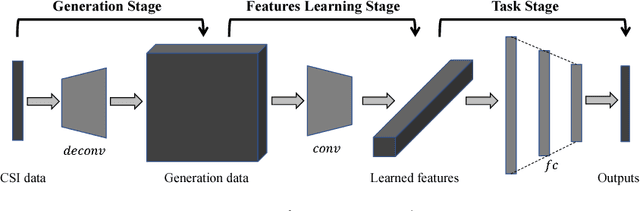
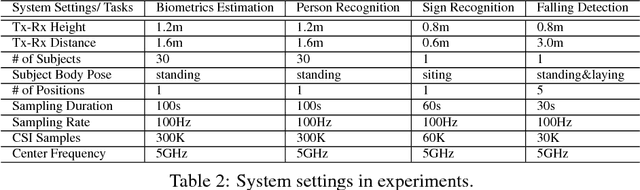
Channel State Information (CSI) of WiFi signals becomes increasingly attractive in human sensing applications due to the pervasiveness of WiFi, robustness to illumination and view points, and little privacy concern comparing to cameras. In majority of existing works, CSI sequences are analyzed by traditional signal processing approaches. These approaches rely on strictly imposed assumption on propagation paths, reflection and attenuation of signal interacting with human bodies and indoor background. This makes existing approaches very difficult to model the delicate body characteristics and activities in the real applications. To address these issues, we build CSI-Net, a unified Deep Neural Network (DNN), that fully utilizes the strength of deep feature representation and the power of existing DNN architectures for CSI-based human sensing problems. Using CSI-Net, we jointly solved two body characterization problems: biometrics estimation (including body fat, muscle, water and bone rates) and human identification. We also demonstrated the application of CSI-Net on two distinctive action recognition tasks: the hand sign recognition (fine-scaled action of the hand) and falling detection (coarse-scaled motion of the body). Besides the technical contribution of CSI-Net, we present major discoveries and insights on how the multi-frequency CSI signals are encoded and processed in DNNs, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first attempt that bridges the WiFi sensing and deep learning in human sensing problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge