Cross-sensor Pore Detection in High-resolution Fingerprint Images using Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
Aug 28, 2019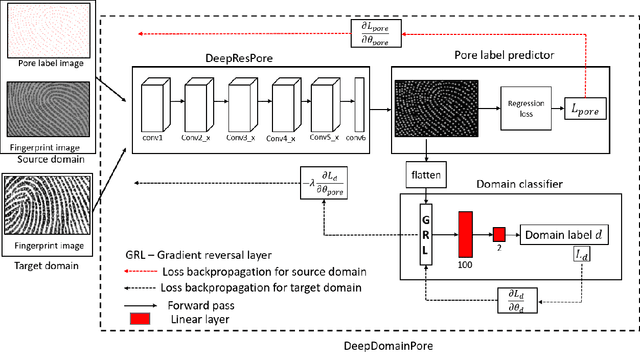



With the emergence of the high-resolution fingerprint sensors, the research community has focused on level-3 fingerprint features especially, pores for providing the next generation automated fingerprint recognition system (AFRS). Following the recent success of the deep learning approaches in various computer vision tasks, researchers have explored learning-based approaches for pore detection in high-resolution fingerprint images. These learning-based approaches provide better performance than the hand-crafted feature-based approaches. However, domain adaptability of existing learning-based pore detection methods has not been examined in the past. In this paper, we present the first study of domain adaptability of existing learning-based pore detection methods. For this purpose, we have generated an in-house ground truth dataset referred to as IITI-HRF-GT by using 1000 dpi fingerprint sensor and evaluated the performance of the existing learning-based pore detection approaches on it. Further, we have also proposed an approach for detecting pores in a cross sensor scenario referred to as DeepDomainPore using unsupervised domain adaptation technique. Specifically, DeepDomainPore is a combination of a convolutional neural network (CNN) based pore detection approach DeepResPore and an unsupervised domain adaptation approach included during the training process. The domain adaptation in the DeepDomainPore is achieved by embedding a gradient reversal layer between the DeepResPore and a domain classifier network. The results of all the existing and the proposed learning-based pore detection approaches are evaluated on IITI-HRF-GT. The DeepDomainPore provides a true detection rate of 88.09%and an F-score of 83.94% on IITI-HRF-GT. Most importantly, the proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the cross sensor dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge