Counterfactual Language Model Adaptation for Suggesting Phrases
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2017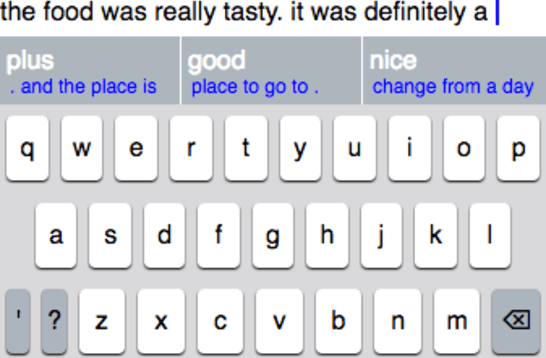

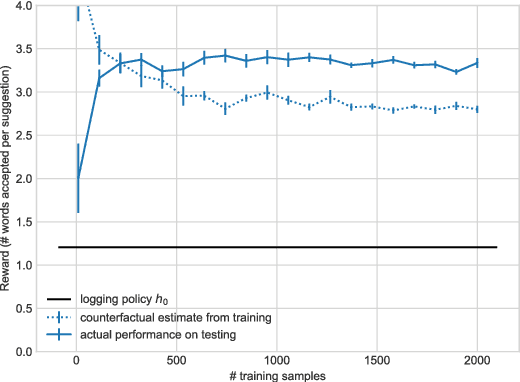
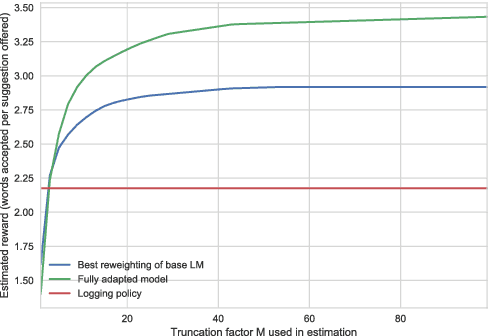
Mobile devices use language models to suggest words and phrases for use in text entry. Traditional language models are based on contextual word frequency in a static corpus of text. However, certain types of phrases, when offered to writers as suggestions, may be systematically chosen more often than their frequency would predict. In this paper, we propose the task of generating suggestions that writers accept, a related but distinct task to making accurate predictions. Although this task is fundamentally interactive, we propose a counterfactual setting that permits offline training and evaluation. We find that even a simple language model can capture text characteristics that improve acceptability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge