Constructing transient amplifiers for death-Birth updating: A case study of cubic and quartic regular graphs
Paper and Code
Aug 04, 2020
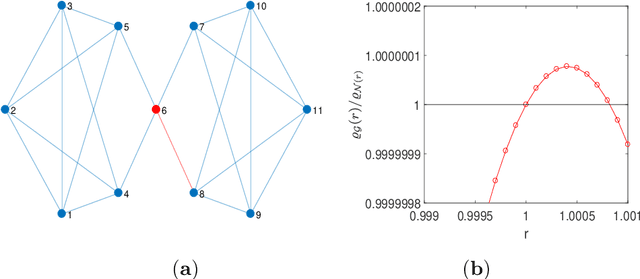


A central question of evolutionary dynamics on graphs is whether or not a mutation introduced in a population of residents survives and eventually even spreads to the whole population, or gets extinct. The outcome naturally depends on the fitness of the mutant and the rules by which mutants and residents may propagate on the network, but arguably the most determining factor is the network structure. Some structured networks are transient amplifiers. They increase for a certain fitness range the fixation probability of beneficial mutations as compared to a well-mixed population. We study a perturbation methods for identifying transient amplifiers for death-Birth updating. The method includes calculating the coalescence times of random walks on graphs and finding the vertex with the largest remeeting time. If the graph is perturbed by removing an edge from this vertex, there is a certain likelihood that the resulting perturbed graph is a transient amplifier. We test all pairwise nonisomorphic cubic and quartic regular graphs up to a certain size and thus cover the whole structural range expressible by these graphs. We carry out a spectral analysis and show that the graphs from which the transient amplifiers can be constructed share certain structural properties. The graphs are path-like, have low conductance and are rather easy to divide into subgraphs by removing edges and/or vertices. This is connected with the subgraphs being identical (or almost identical) building blocks and the frequent occurrence of cut and/or hinge vertices. Identifying spectral and structural properties may promote finding and designing such networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge