Constructing Dynamic Treatment Regimes in Infinite-Horizon Settings
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2015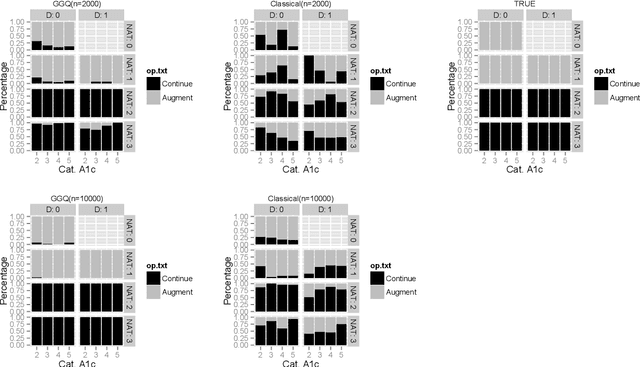
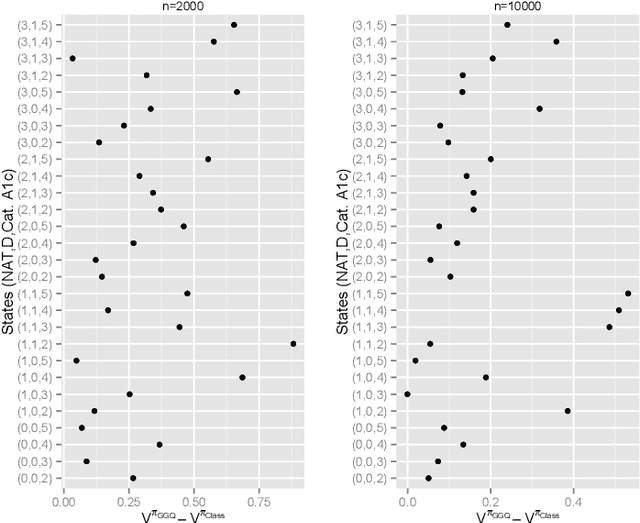
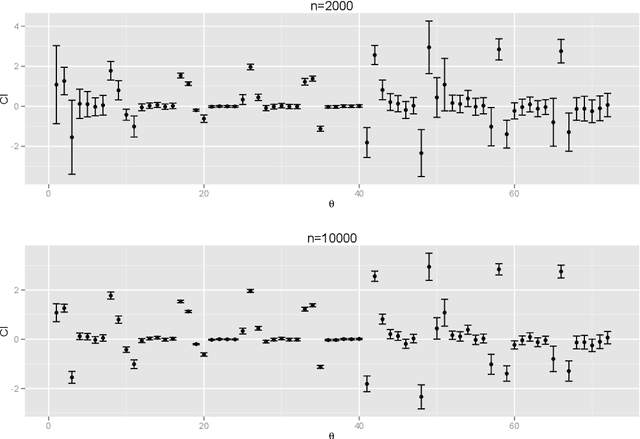
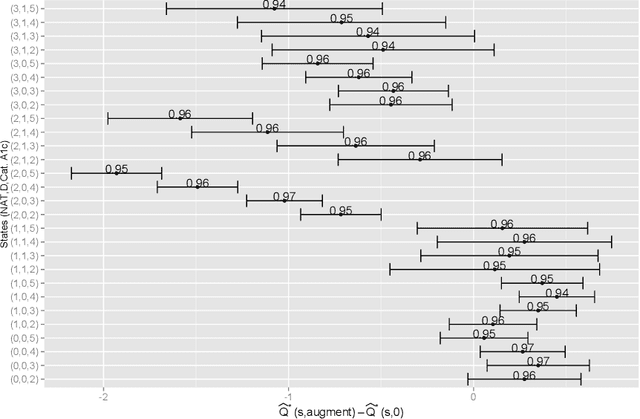
The application of existing methods for constructing optimal dynamic treatment regimes is limited to cases where investigators are interested in optimizing a utility function over a fixed period of time (finite horizon). In this manuscript, we develop an inferential procedure based on temporal difference residuals for optimal dynamic treatment regimes in infinite-horizon settings, where there is no a priori fixed end of follow-up point. The proposed method can be used to determine the optimal regime in chronic diseases where patients are monitored and treated throughout their life. We derive large sample results necessary for conducting inference. We also simulate a cohort of patients with diabetes to mimic the third wave of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, and we examine the performance of the proposed method in controlling the level of hemoglobin A1c. Supplementary materials for this article are available online.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge