Conquering the CNN Over-Parameterization Dilemma: A Volterra Filtering Approach for Action Recognition
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2019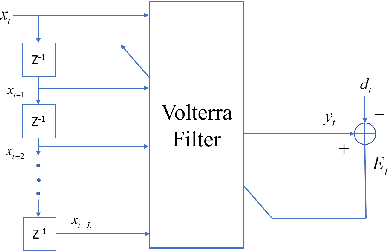
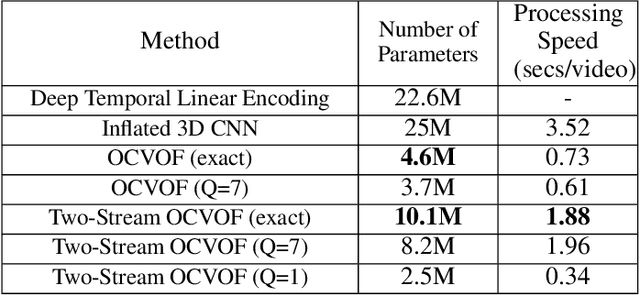


The importance of inference in Machine Learning (ML) has led to an explosive number of different proposals in ML, and particularly in Deep Learning. In an attempt to reduce the complexity of Convolutional Neural Networks, we propose a Volterra filter-inspired Network architecture. This architecture introduces controlled non-linearities in the form of interactions between the delayed input samples of data. We propose a cascaded implementation of Volterra Filter so as to significantly reduce the number of parameters required to carry out the same classification task as that of a conventional Neural Network. We demonstrate an efficient parallel implementation of this new Volterra network, along with its remarkable performance while retaining a relatively simpler and potentially more tractable structure. Furthermore, we show a rather sophisticated adaptation of this network to nonlinearly fuse the RGB (spatial) information and the Optical Flow (temporal) information of a video sequence for action recognition. The proposed approach is evaluated on UCF-101 and HMDB-51 datasets for action recognition, and is shown to outperform state of the art when trained on the datasets from scratch (i.e. without pre-training on a larger dataset).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge