Connections between Relational Event Model and Inverse Reinforcement Learning for Characterizing Group Interaction Sequences
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2020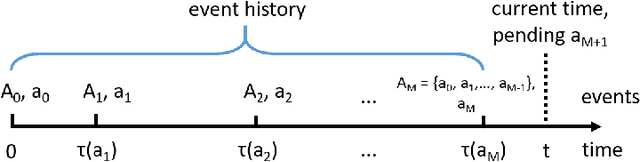
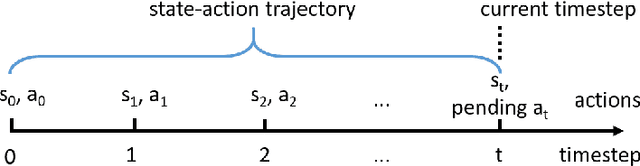
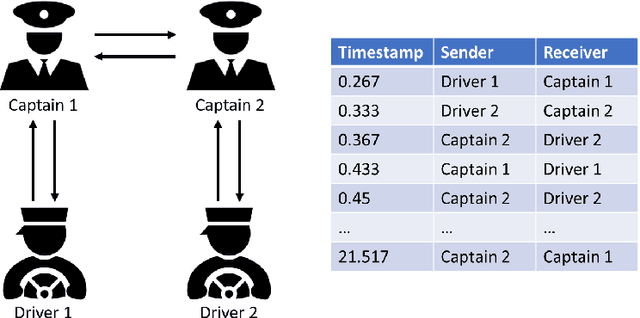
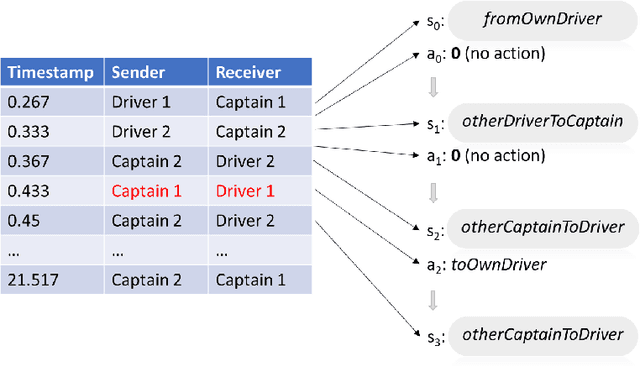
In this paper we explore previously unidentified connections between relational event model (REM) from the field of network science and inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) from the field of machine learning with respect to their ability to characterize sequences of directed social interaction events in group settings. REM is a conventional approach to tackle such a problem whereas the application of IRL is a largely unbeaten path. We begin by examining the mathematical components of both REM and IRL and find straightforward analogies between the two methods as well as unique characteristics of the IRL approach. We demonstrate the special utility of IRL in characterizing group social interactions with an empirical experiment, in which we use IRL to infer individual behavioral preferences based on a sequence of directed communication events from a group of virtual-reality game players interacting and cooperating to accomplish a shared goal. Our comparison and experiment introduce fresh perspectives for social behavior analytics and help inspire new research opportunities at the nexus of social network analysis and machine learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge