Conflict-Based Search for Explainable Multi-Agent Path Finding
Paper and Code
Feb 20, 2022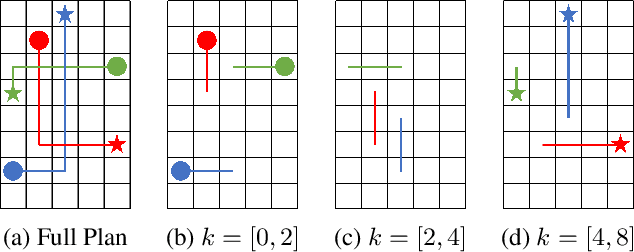
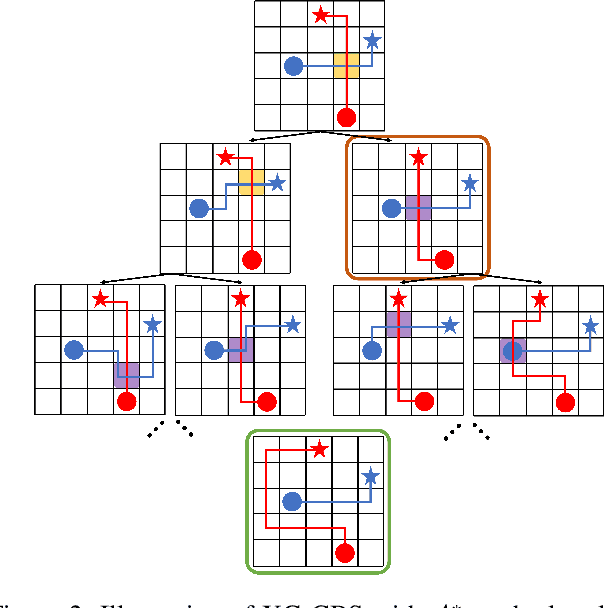
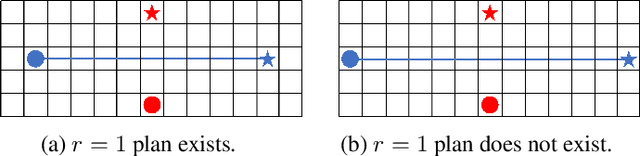
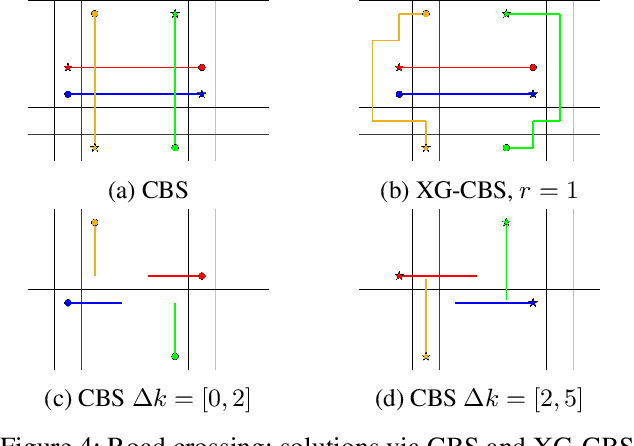
In the Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) problem, the goal is to find non-colliding paths for agents in an environment, such that each agent reaches its goal from its initial location. In safety-critical applications, a human supervisor may want to verify that the plan is indeed collision-free. To this end, a recent work introduces a notion of explainability for MAPF based on a visualization of the plan as a short sequence of images representing time segments, where in each time segment the trajectories of the agents are disjoint. Then, the explainable MAPF problem asks for a set of non-colliding paths that admits a short-enough explanation. Explainable MAPF adds a new difficulty to MAPF, in that it is NP-hard with respect to the size of the environment, and not just the number of agents. Thus, traditional MAPF algorithms are not equipped to directly handle explainable-MAPF. In this work, we adapt Conflict Based Search (CBS), a well-studied algorithm for MAPF, to handle explainable MAPF. We show how to add explainability constraints on top of the standard CBS tree and its underlying A* search. We examine the usefulness of this approach and, in particular, the tradeoff between planning time and explainability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge