Comprehensive Study on Denoising of Medical Images Utilizing Neural Network Based Auto-Encoder
Paper and Code
Feb 03, 2021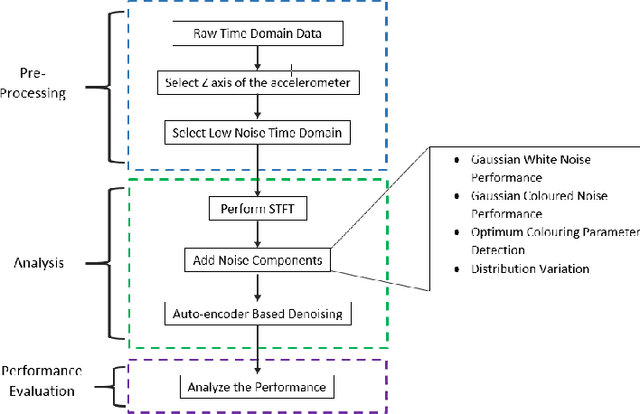
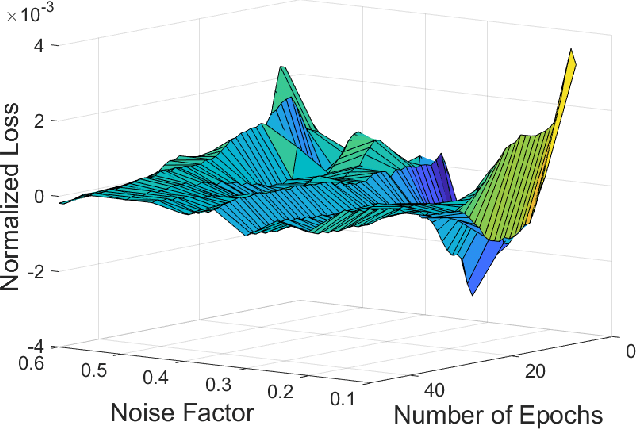
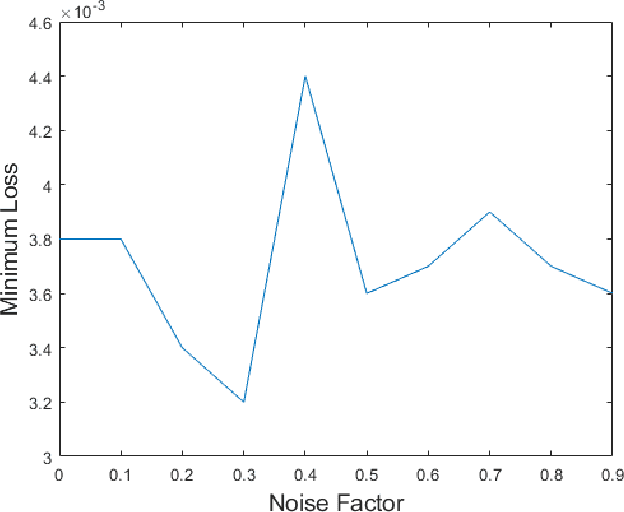
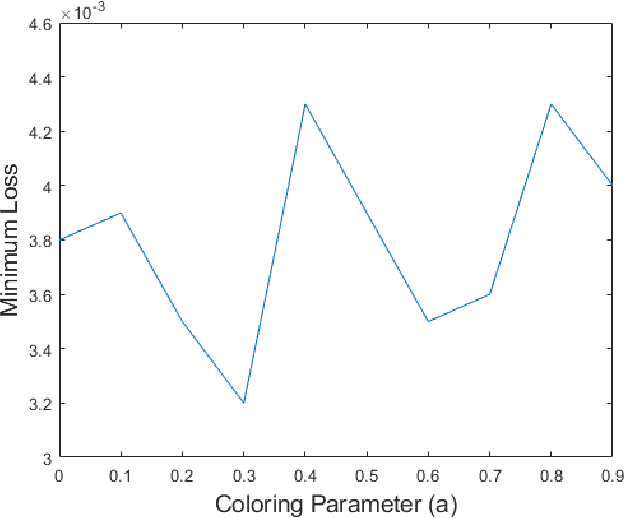
Fetal motion discernment utilizing spectral images extracted from accelerometric data incident on pregnant mothers abdomen has gained substantial attention in the state-of-the-art research. It is an essential practice to avoid adverse scenarios such as stillbirths and intrauterine growth restrictions. However, this endeavor of ensuring fetus safety has been arduous due to the existence of random noise in medical images. This novel research is an in depth approach to analyze how the interference of different noise variations affect the retrieval of information in those images. For that, an algorithm employing auto-encoder-based deep learning was modeled and the accuracy of reconstruction of the STFT images mitigating the noise has been measured examining the loss. From the results, it is manifested that even a substantial addition of the Super-Gaussian noises which have a higher correlation of the frequencies possessed by the Fetal movement images can be restored successfully with the slightest error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge