Community Detection in the Stochastic Block Model by Mixed Integer Programming
Paper and Code
Jan 26, 2021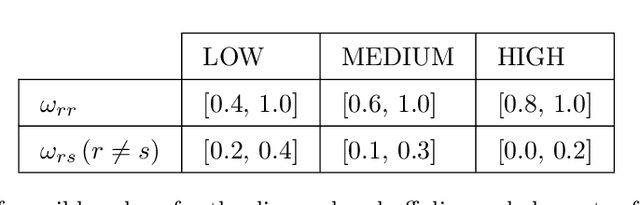
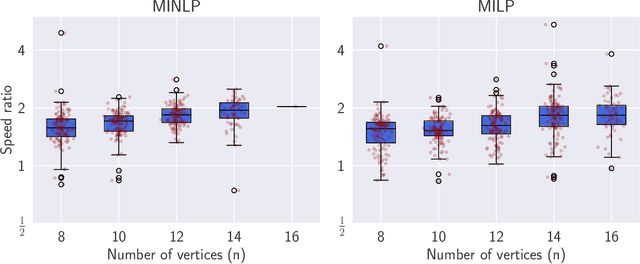
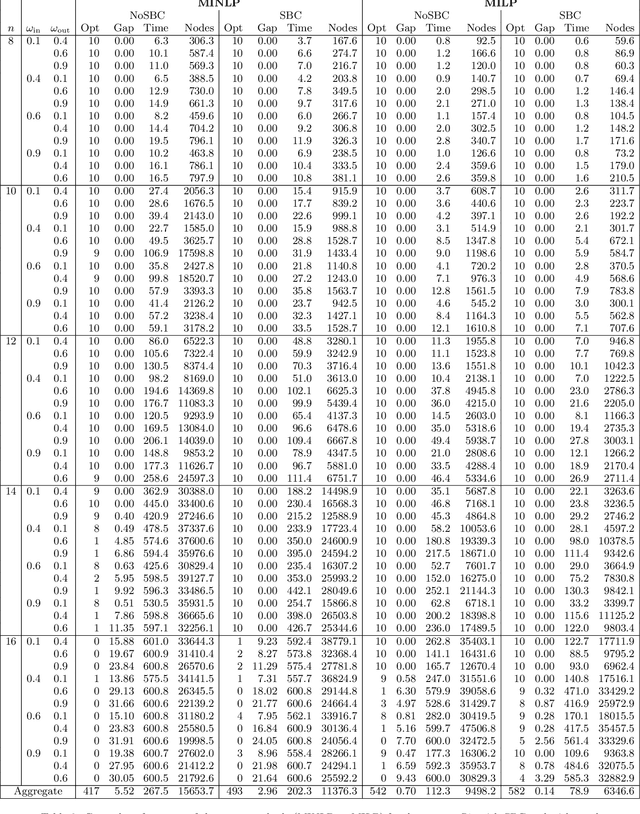
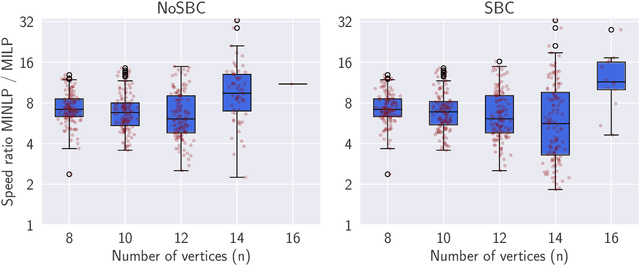
The Degree-Corrected Stochastic Block Model (DCSBM) is a popular model to generate random graphs with community structure given an expected degree sequence. The standard approach of community detection based on the DCSBM is to search for the model parameters that are the most likely to have produced the observed network data through maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). Current techniques for the MLE problem are heuristics, and therefore do not guarantee convergence to the optimum. We present mathematical programming formulations and exact solution methods that can provably find the model parameters and community assignments of maximum likelihood given an observed graph. We compare these exact methods with classical heuristic algorithms based on expectation-maximization (EM). The solutions given by exact methods give us a principled way of measuring the experimental performance of classical heuristics and comparing different variations thereof.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge