Communication Traffic Characteristics Reveal an IoT Devices Identity
Paper and Code
Feb 25, 2024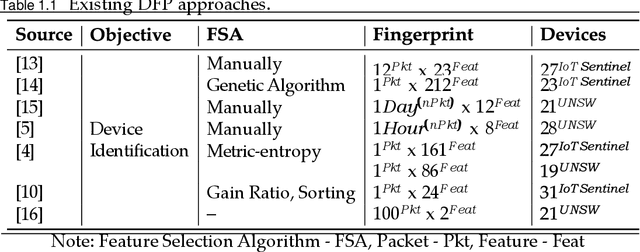
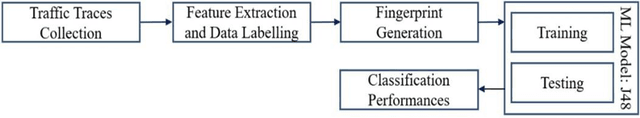

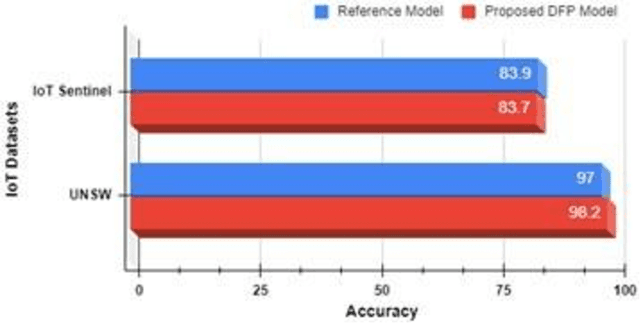
Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the technological advancements of the twenty-first century which can improve living standards. However, it also imposes new types of security challenges, including device authentication, traffic types classification, and malicious traffic identification, in the network domain. Traditionally, internet protocol (IP) and media access control (MAC) addresses are utilized for identifying network-connected devices in a network, whilst these addressing schemes are prone to be compromised, including spoofing attacks and MAC randomization. Therefore, device identification using only explicit identifiers is a challenging task. Accurate device identification plays a key role in securing a network. In this paper, a supervised machine learning-based device fingerprinting (DFP) model has been proposed for identifying network-connected IoT devices using only communication traffic characteristics (or implicit identifiers). A single transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet header features have been utilized for generating unique fingerprints, with the fingerprints represented as a vector of 22 features. Experimental results have shown that the proposed DFP method achieves over 98% in classifying individual IoT devices using the UNSW dataset with 22 smart-home IoT devices. This signifies that the proposed approach is invaluable to network operators in making their networks more secure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge