Combining Forensics and Privacy Requirements for Digital Images
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2021
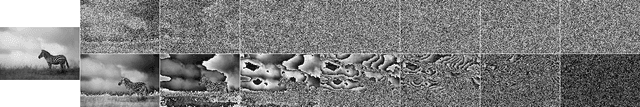

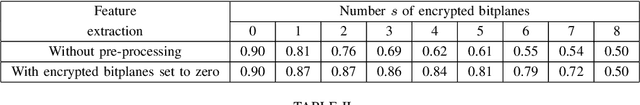
This paper proposes to study the impact of image selective encryption on both forensics and privacy preserving mechanisms. The proposed selective encryption scheme works independently on each bitplane by encrypting the s most significant bits of each pixel. We show that this mechanism can be used to increase privacy by mitigating image recognition tasks. In order to guarantee a trade-off between forensics analysis and privacy, the signal of interest used for forensics purposes is extracted from the 8--s least significant bits of the protected image. We show on the CASIA2 database that good tampering detection capabilities can be achieved for s $\in$ {3,. .. , 5} with an accuracy above 80% using SRMQ1 features, while preventing class recognition tasks using CNN with an accuracy smaller than 50%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge