Combining Control Barrier Functions and Behavior Trees for Multi-Agent Underwater Coverage Missions
Paper and Code
Aug 21, 2020
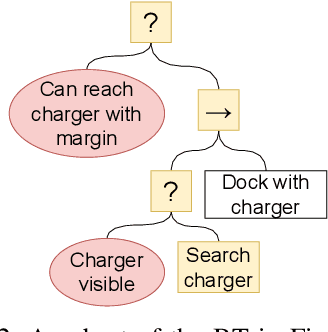

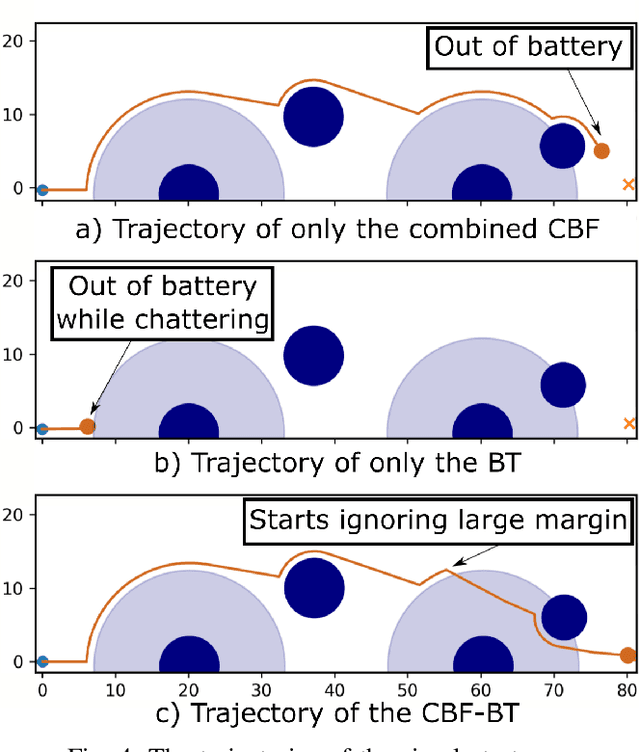
Robot missions typically involve a number of desired objectives, such as avoiding collisions, staying connected to other robots, gathering information using sensors and returning to the charging station before the battery runs out. Some of these objectives need to be taken into account at the same time, such as avoiding collisions and staying connected, while others are focused upon during different parts of the executions, such as returning to the charging station and connectivity maintenance. In this paper, we show how Control Barrier Functions(CBFs) and Behavior Trees(BTs) can be combined in a principled manner to achieve both types of task compositions, with performance guarantees in terms of mission completion. We illustrate our method with a simulated underwater coverage mission.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge