Colonoscopy Landmark Detection using Vision Transformers
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2022
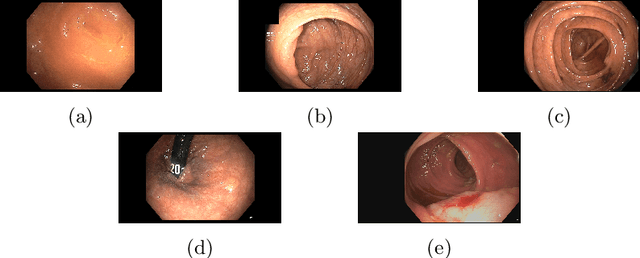
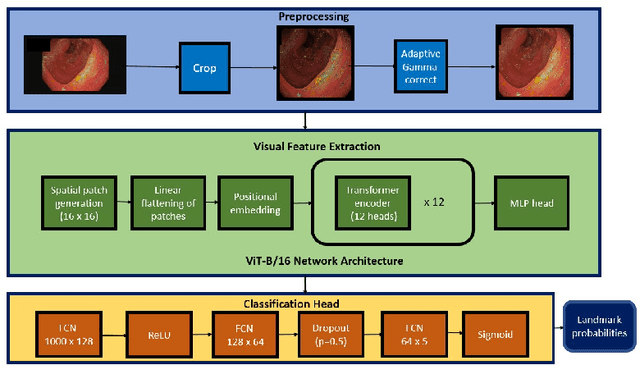
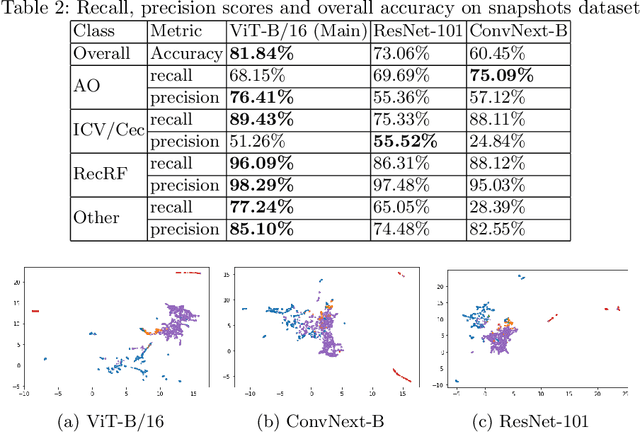
Colonoscopy is a routine outpatient procedure used to examine the colon and rectum for any abnormalities including polyps, diverticula and narrowing of colon structures. A significant amount of the clinician's time is spent in post-processing snapshots taken during the colonoscopy procedure, for maintaining medical records or further investigation. Automating this step can save time and improve the efficiency of the process. In our work, we have collected a dataset of 120 colonoscopy videos and 2416 snapshots taken during the procedure, that have been annotated by experts. Further, we have developed a novel, vision-transformer based landmark detection algorithm that identifies key anatomical landmarks (the appendiceal orifice, ileocecal valve/cecum landmark and rectum retroflexion) from snapshots taken during colonoscopy. Our algorithm uses an adaptive gamma correction during preprocessing to maintain a consistent brightness for all images. We then use a vision transformer as the feature extraction backbone and a fully connected network based classifier head to categorize a given frame into four classes: the three landmarks or a non-landmark frame. We compare the vision transformer (ViT-B/16) backbone with ResNet-101 and ConvNext-B backbones that have been trained similarly. We report an accuracy of 82% with the vision transformer backbone on a test dataset of snapshots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge