Cognitive Homeostatic Agents
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2021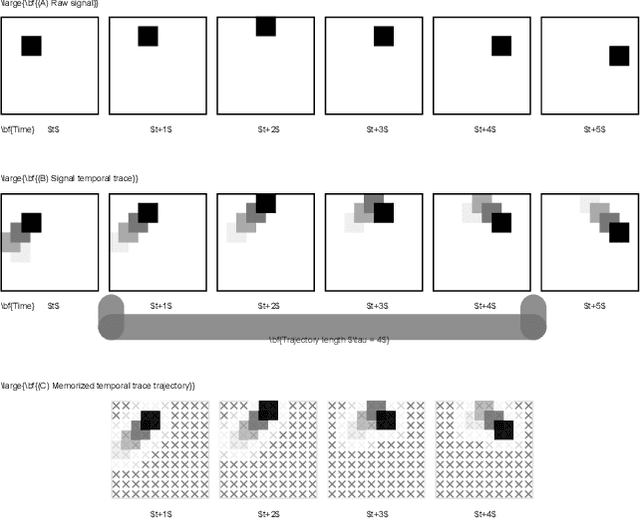
Human brain has been used as an inspiration for building autonomous agents, but it is not obvious what level of computational description of the brain one should use. This has led to overly opinionated symbolic approaches and overly unstructured connectionist approaches. We propose that using homeostasis as the computational description provides a good compromise. Similar to how physiological homeostasis is the regulation of certain homeostatic variables, cognition can be interpreted as the regulation of certain 'cognitive homeostatic variables'. We present an outline of a Cognitive Homeostatic Agent, built as a hierarchy of physiological and cognitive homeostatic subsystems and describe structures and processes to guide future exploration. We expect this to be a fruitful line of investigation towards building sophisticated artificial agents that can act flexibly in complex environments, and produce behaviors indicating planning, thinking and feelings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge