Cluster Flow: how a hierarchical clustering layer make allows deep-NNs more resilient to hacking, more human-like and easily implements relational reasoning
Paper and Code
Apr 27, 2023
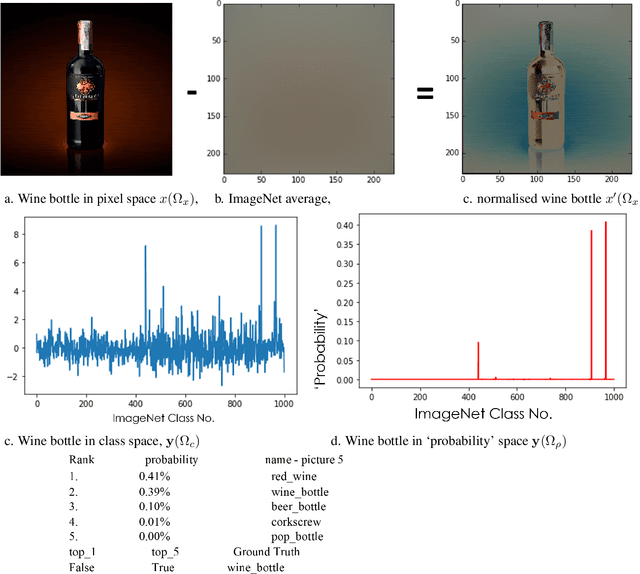
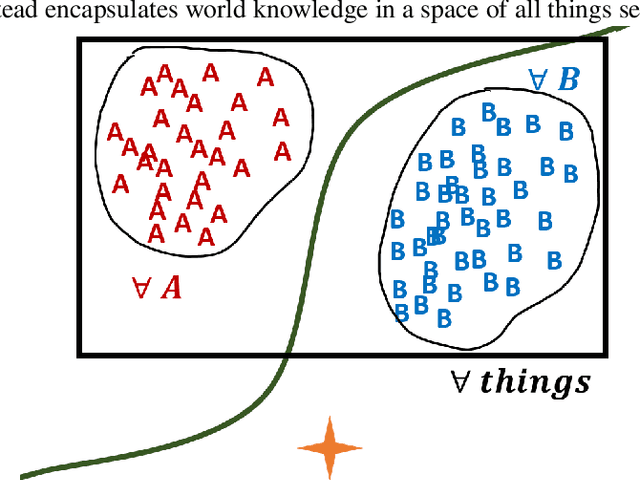
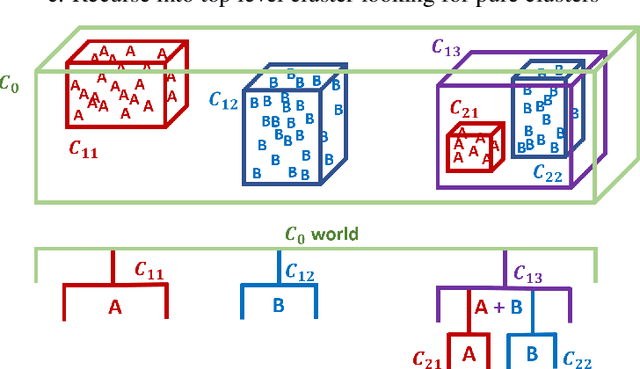
Despite the huge recent breakthroughs in neural networks (NNs) for artificial intelligence (specifically deep convolutional networks) such NNs do not achieve human-level performance: they can be hacked by images that would fool no human and lack `common sense'. It has been argued that a basis of human-level intelligence is mankind's ability to perform relational reasoning: the comparison of different objects, measuring similarity, grasping of relations between objects and the converse, figuring out the odd one out in a set of objects. Mankind can even do this with objects they have never seen before. Here we show how ClusterFlow, a semi-supervised hierarchical clustering framework can operate on trained NNs utilising the rich multi-dimensional class and feature data found at the pre-SoftMax layer to build a hyperspacial map of classes/features and this adds more human-like functionality to modern deep convolutional neural networks. We demonstrate this with 3 tasks. 1. the statistical learning based `mistakes' made by infants when attending to images of cats and dogs. 2. improving both the resilience to hacking images and the accurate measure of certainty in deep-NNs. 3. Relational reasoning over sets of images, including those not known to the NN nor seen before. We also demonstrate that ClusterFlow can work on non-NN data and deal with missing data by testing it on a Chemistry dataset. This work suggests that modern deep NNs can be made more human-like without re-training of the NNs. As it is known that some methods used in deep and convolutional NNs are not biologically plausible or perhaps even the best approach: the ClusterFlow framework can sit on top of any NN and will be a useful tool to add as NNs are improved in this regard.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge