Child PalmID: Contactless Palmprint Recognition
Paper and Code
Dec 14, 2022
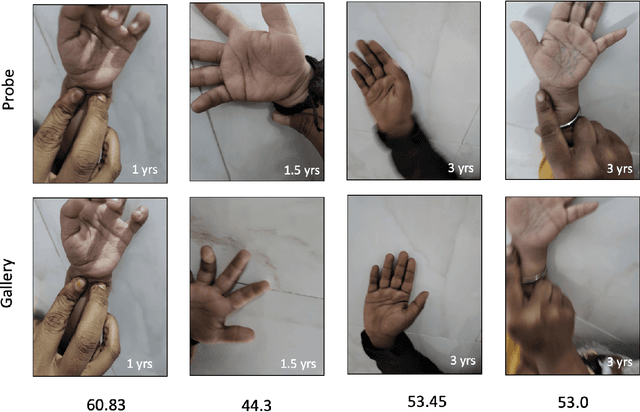

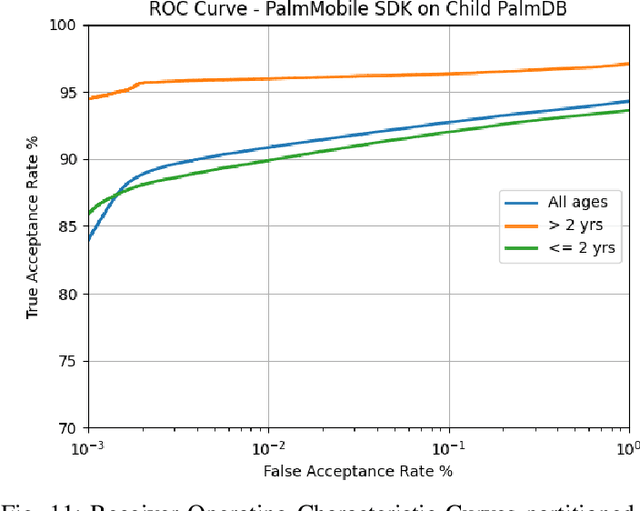

Developing and least developed countries face the dire challenge of ensuring that each child in their country receives required doses of vaccination, adequate nutrition and proper medication. International agencies such as UNICEF, WHO and WFP, among other organizations, strive to find innovative solutions to determine which child has received the benefits and which have not. Biometric recognition systems have been sought out to help solve this problem. To that end, this report establishes a baseline accuracy of a commercial contactless palmprint recognition system that may be deployed for recognizing children in the age group of one to five years old. On a database of contactless palmprint images of one thousand unique palms from 500 children, we establish SOTA authentication accuracy of 90.85% @ FAR of 0.01%, rank-1 identification accuracy of 99.0% (closed set), and FPIR=0.01 @ FNIR=0.3 for open-set identification using PalmMobile SDK from Armatura.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge