Channel Gain Cartography via Mixture of Experts
Paper and Code
Dec 08, 2020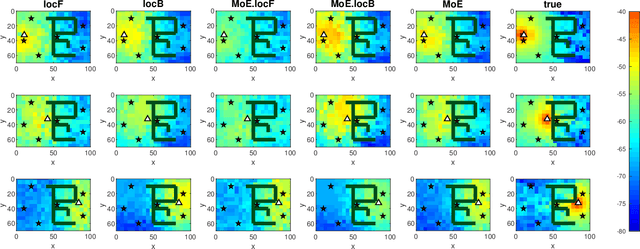
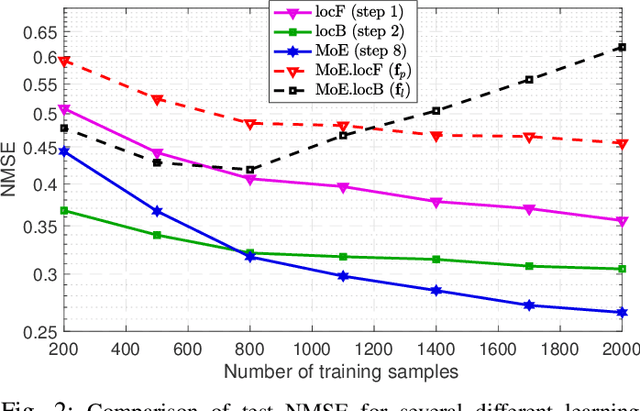
In order to estimate the channel gain (CG) between the locations of an arbitrary transceiver pair across a geographic area of interest, CG maps can be constructed from spatially distributed sensor measurements. Most approaches to build such spectrum maps are location-based, meaning that the input variable to the estimating function is a pair of spatial locations. The performance of such maps depends critically on the ability of the sensors to determine their positions, which may be drastically impaired if the positioning pilot signals are affected by multi-path channels. An alternative location-free approach was recently proposed for spectrum power maps, where the input variable to the maps consists of features extracted from the positioning signals, instead of location estimates. The location-based and the location-free approaches have complementary merits. In this work, apart from adapting the location-free features for the CG maps, a method that can combine both approaches is proposed in a mixture-of-experts framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge