Challenges and Limitations with the Metrics Measuring the Complexity of Code-Mixed Text
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2021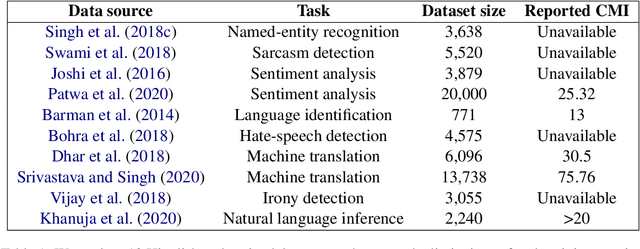

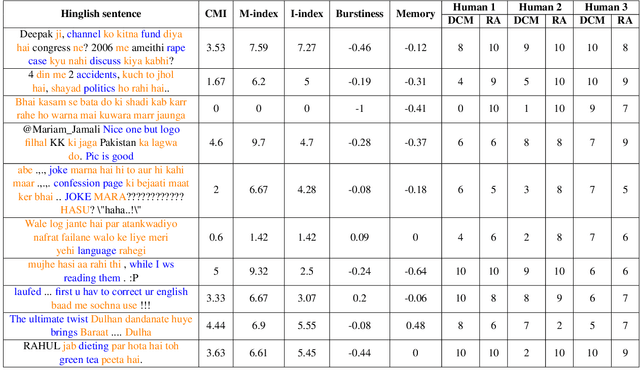

Code-mixing is a frequent communication style among multilingual speakers where they mix words and phrases from two different languages in the same utterance of text or speech. Identifying and filtering code-mixed text is a challenging task due to its co-existence with monolingual and noisy text. Over the years, several code-mixing metrics have been extensively used to identify and validate code-mixed text quality. This paper demonstrates several inherent limitations of code-mixing metrics with examples from the already existing datasets that are popularly used across various experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge