Centralized and Federated Heart Disease Classification Models Using UCI Dataset and their Shapley-value Based Interpretability
Paper and Code
Aug 12, 2024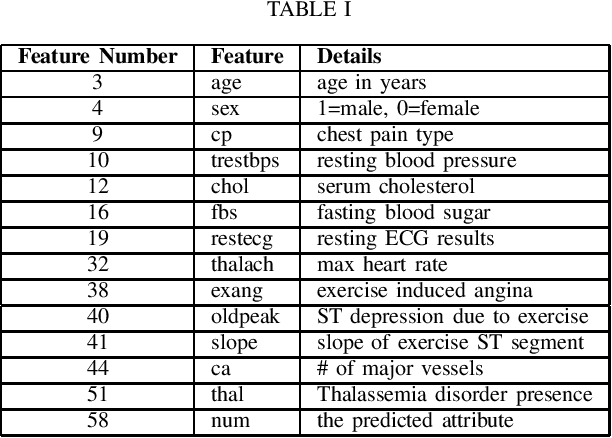
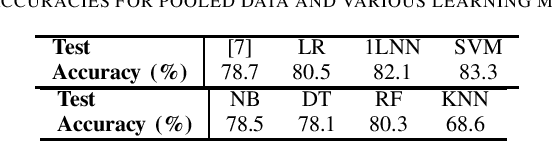
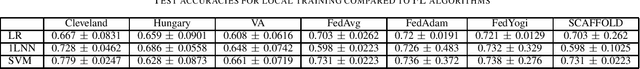
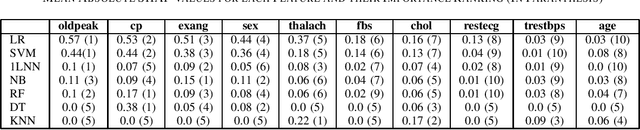
Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of mortality worldwide, highlighting the need for accurate diagnostic methods. This study benchmarks centralized and federated machine learning algorithms for heart disease classification using the UCI dataset which includes 920 patient records from four hospitals in the USA, Hungary and Switzerland. Our benchmark is supported by Shapley-value interpretability analysis to quantify features' importance for classification. In the centralized setup, various binary classification algorithms are trained on pooled data, with a support vector machine (SVM) achieving the highest testing accuracy of 83.3\%, surpassing the established benchmark of 78.7\% with logistic regression. Additionally, federated learning algorithms with four clients (hospitals) are explored, leveraging the dataset's natural partition to enhance privacy without sacrificing accuracy. Federated SVM, an uncommon approach in the literature, achieves a top testing accuracy of 73.8\%. Our interpretability analysis aligns with existing medical knowledge of heart disease indicators. Overall, this study establishes a benchmark for efficient and interpretable pre-screening tools for heart disease while maintaining patients' privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge