Causal Network Influence with Latent Homophily and Measurement Error: An Application to Therapeutic Community
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2022

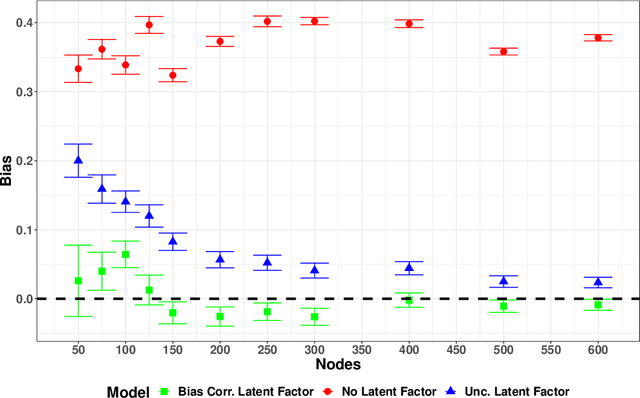

The Spatial or Network Autoregressive model (SAR, NAM) is popular for modeling the influence network connected neighbors exert on the outcome of individuals. However, many authors have noted that the \textit{causal} network influence or contagion cannot be identified from observational data due to the presence of homophily. We propose a latent homophily-adjusted spatial autoregressive model for networked responses to identify the causal contagion and contextual effects. The latent homophily is estimated from the spectral embedding of the network's adjacency matrix. Separately, we develop maximum likelihood estimators for the parameters of the SAR model correcting for measurement error when covariates are measured with error. We show that the bias corrected MLE are consistent and derive its asymptotic limiting distribution. We propose to estimate network influence using the bias corrected MLE in a SAR model with the estimated latent homophily added as a covariate. Our simulations show that the methods perform well in finite sample. We apply our methodology to a data-set of female criminal offenders in a therapeutic community (TC) for substance abuse and criminal behavior. We provide causal estimates of network influence on graduation from TC and re-incarceration after accounting for latent homophily.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge