Causal Interaction Trees: Tree-Based Subgroup Identification for Observational Data
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2020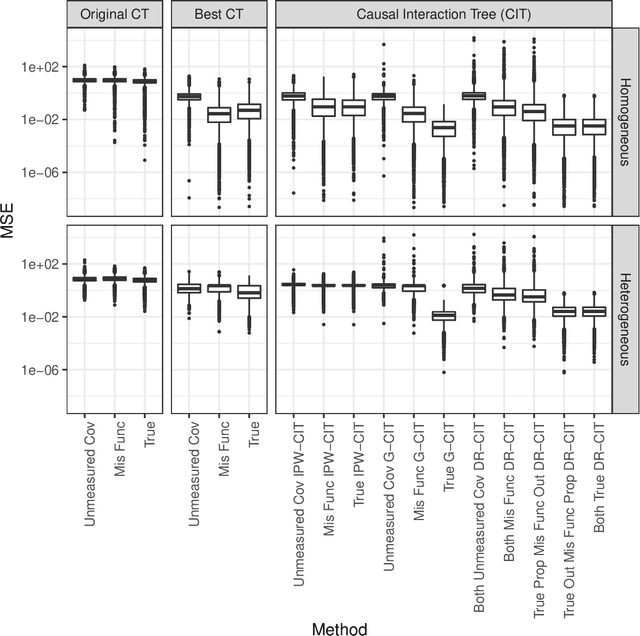
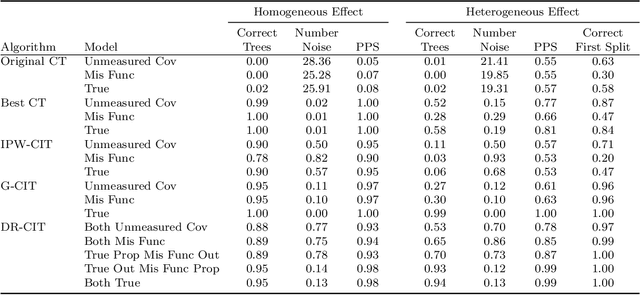
We propose Causal Interaction Trees for identifying subgroups of participants that have enhanced treatment effects using observational data. We extend the Classification and Regression Tree algorithm by using splitting criteria that focus on maximizing between-group treatment effect heterogeneity based on subgroup-specific treatment effect estimators to dictate decision-making in the algorithm. We derive properties of three subgroup-specific treatment effect estimators that account for the observational nature of the data -- inverse probability weighting, g-formula and doubly robust estimators. We study the performance of the proposed algorithms using simulations and implement the algorithms in an observational study that evaluates the effectiveness of right heart catheterization on critically ill patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge