Causal Inference through a Witness Protection Program
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2014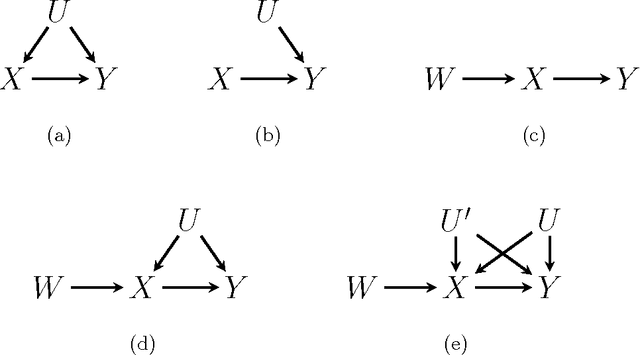
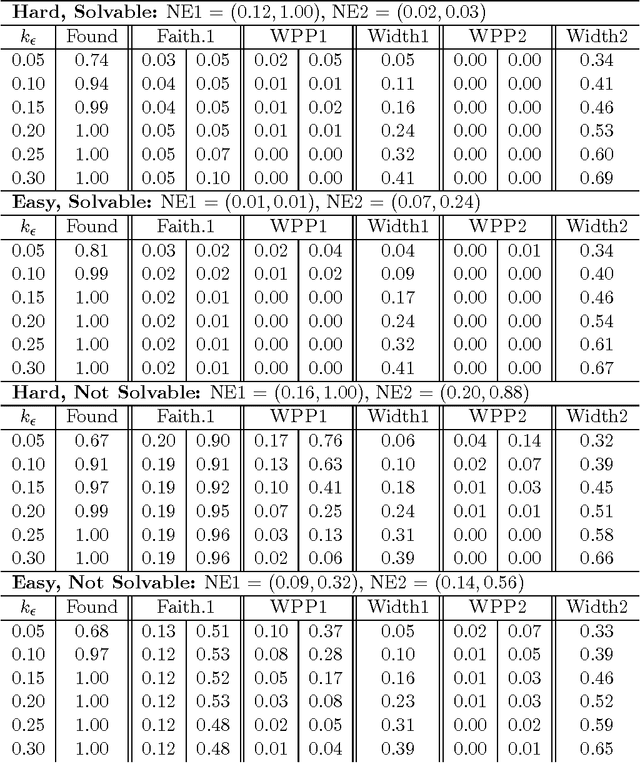
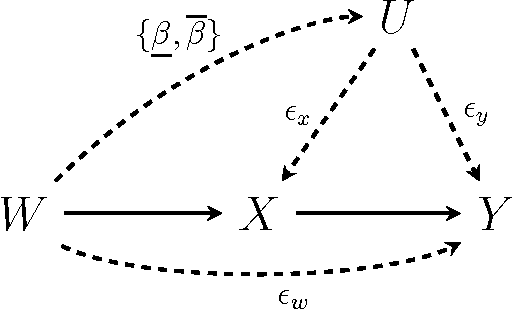
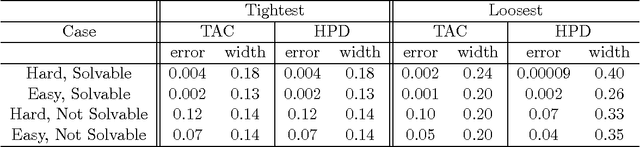
One of the most fundamental problems in causal inference is the estimation of a causal effect when variables are confounded. This is difficult in an observational study, because one has no direct evidence that all confounders have been adjusted for. We introduce a novel approach for estimating causal effects that exploits observational conditional independencies to suggest "weak" paths in a unknown causal graph. The widely used faithfulness condition of Spirtes et al. is relaxed to allow for varying degrees of "path cancellations" that imply conditional independencies but do not rule out the existence of confounding causal paths. The outcome is a posterior distribution over bounds on the average causal effect via a linear programming approach and Bayesian inference. We claim this approach should be used in regular practice along with other default tools in observational studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge