Causal Discovery on the Effect of Antipsychotic Drugs on Delirium Patients in the ICU using Large EHR Dataset
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2022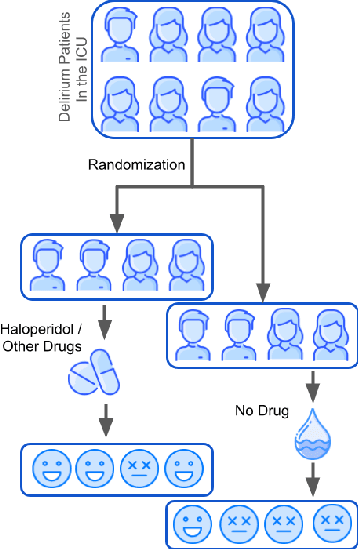

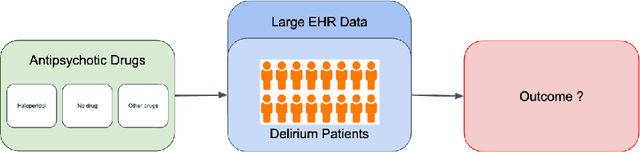

Delirium occurs in about 80% cases in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and is associated with a longer hospital stay, increased mortality and other related issues. Delirium does not have any biomarker-based diagnosis and is commonly treated with antipsychotic drugs (APD). However, multiple studies have shown controversy over the efficacy or safety of APD in treating delirium. Since randomized controlled trials (RCT) are costly and time-expensive, we aim to approach the research question of the efficacy of APD in the treatment of delirium using retrospective cohort analysis. We plan to use the Causal inference framework to look for the underlying causal structure model, leveraging the availability of large observational data on ICU patients. To explore safety outcomes associated with APD, we aim to build a causal model for delirium in the ICU using large observational data sets connecting various covariates correlated with delirium. We utilized the MIMIC III database, an extensive electronic health records (EHR) dataset with 53,423 distinct hospital admissions. Our null hypothesis is: there is no significant difference in outcomes for delirium patients under different drug-group in the ICU. Through our exploratory, machine learning based and causal analysis, we had findings such as: mean length-of-stay and max length-of-stay is higher for patients in Haloperidol drug group, and haloperidol group has a higher rate of death in a year compared to other two-groups. Our generated causal model explicitly shows the functional relationships between different covariates. For future work, we plan to do time-varying analysis on the dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge