Casting Geometric Constraints in Semantic Segmentation as Semi-Supervised Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 30, 2019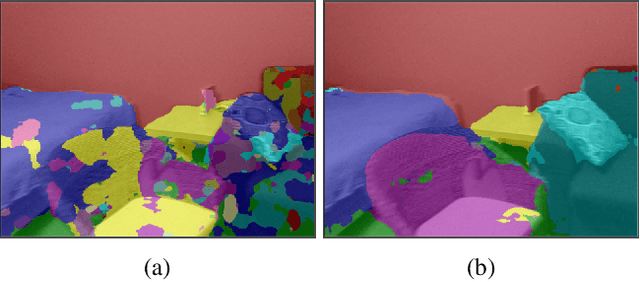
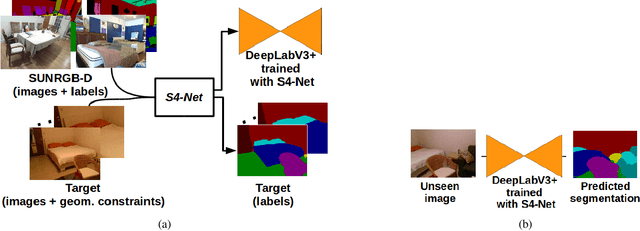

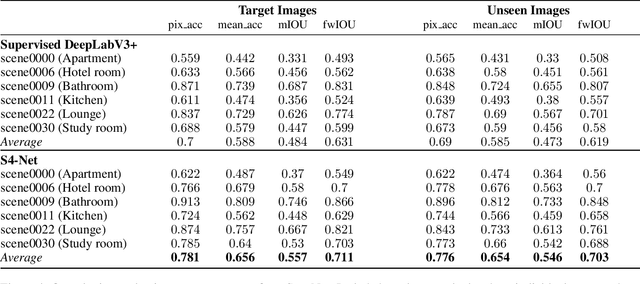
We propose a simple yet effective method to learn to segment new indoor scenes from an RGB-D sequence: State-of-the-art methods trained on one dataset, even as large as SUNRGB-D dataset, can perform poorly when applied to images that are not part of the dataset, because of the dataset bias, a common phenomenon in computer vision. To make semantic segmentation more useful in practice, we learn to segment new indoor scenes from sequences without manual annotations by exploiting geometric constraints and readily available training data from SUNRGB-D. As a result, we can then robustly segment new images of these scenes from color information only. To efficiently exploit geometric constraints for our purpose, we propose to cast these constraints as semi-supervised terms, which enforce the fact that the same class should be predicted for the projections of the same 3D location in different images. We show that this approach results in a simple yet very powerful method, which can annotate sequences of ScanNet and our own sequences using only annotations from SUNRGB-D.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge