Can we integrate spatial verification methods into neural-network loss functions for atmospheric science?
Paper and Code
Mar 21, 2022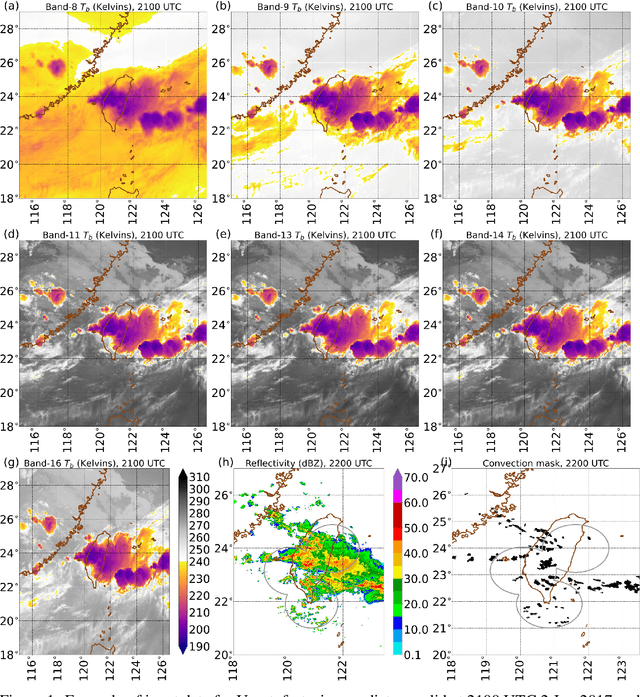
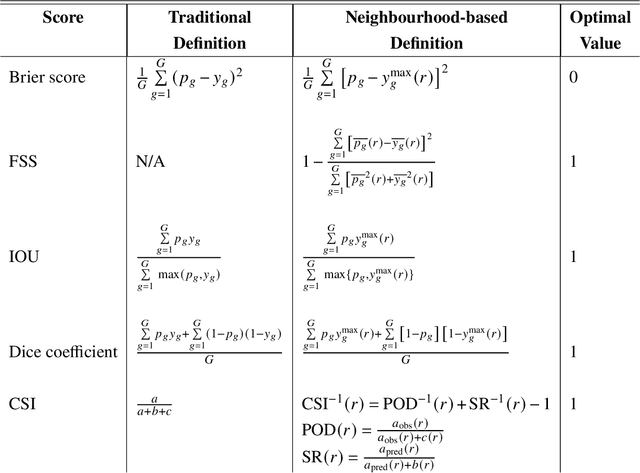
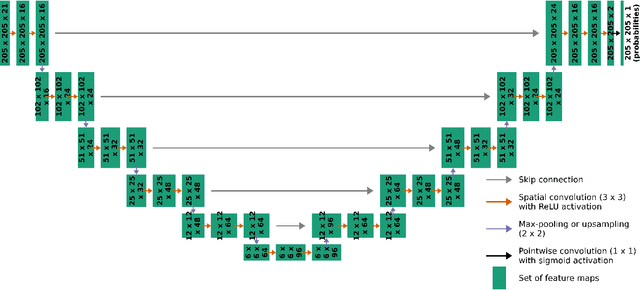
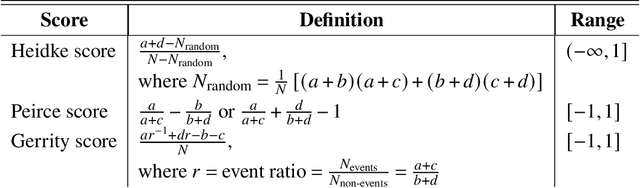
In the last decade, much work in atmospheric science has focused on spatial verification (SV) methods for gridded prediction, which overcome serious disadvantages of pixelwise verification. However, neural networks (NN) in atmospheric science are almost always trained to optimize pixelwise loss functions, even when ultimately assessed with SV methods. This establishes a disconnect between model verification during vs. after training. To address this issue, we develop spatially enhanced loss functions (SELF) and demonstrate their use for a real-world problem: predicting the occurrence of thunderstorms (henceforth, "convection") with NNs. In each SELF we use either a neighbourhood filter, which highlights convection at scales larger than a threshold, or a spectral filter (employing Fourier or wavelet decomposition), which is more flexible and highlights convection at scales between two thresholds. We use these filters to spatially enhance common verification scores, such as the Brier score. We train each NN with a different SELF and compare their performance at many scales of convection, from discrete storm cells to tropical cyclones. Among our many findings are that (a) for a low (high) risk threshold, the ideal SELF focuses on small (large) scales; (b) models trained with a pixelwise loss function perform surprisingly well; (c) however, models trained with a spectral filter produce better-calibrated probabilities than a pixelwise model. We provide a general guide to using SELFs, including technical challenges and the final Python code, as well as demonstrating their use for the convection problem. To our knowledge this is the most in-depth guide to SELFs in the geosciences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge