Can't Boil This Frog: Robustness of Online-Trained Autoencoder-Based Anomaly Detectors to Adversarial Poisoning Attacks
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2020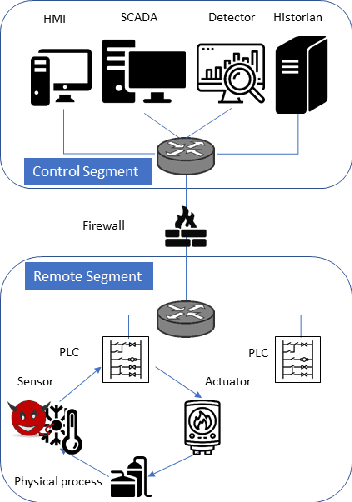
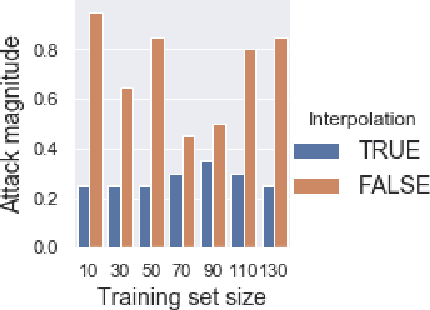
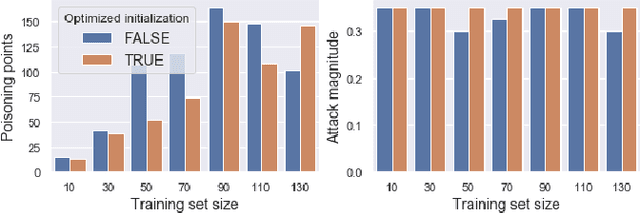
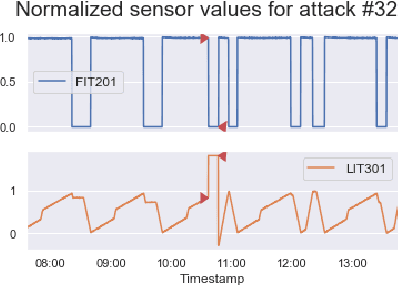
In recent years, a variety of effective neural network-based methods for anomaly and cyber attack detection in industrial control systems (ICSs) have been demonstrated in the literature. Given their successful implementation and widespread use, there is a need to study adversarial attacks on such detection methods to better protect the systems that depend upon them. The extensive research performed on adversarial attacks on image and malware classification has little relevance to the physical system state prediction domain, which most of the ICS attack detection systems belong to. Moreover, such detection systems are typically retrained using new data collected from the monitored system, thus the threat of adversarial data poisoning is significant, however this threat has not yet been addressed by the research community. In this paper, we present the first study focused on poisoning attacks on online-trained autoencoder-based attack detectors. We propose two algorithms for generating poison samples, an interpolation-based algorithm and a back-gradient optimization-based algorithm, which we evaluate on both synthetic and real-world ICS data. We demonstrate that the proposed algorithms can generate poison samples that cause the target attack to go undetected by the autoencoder detector, however the ability to poison the detector is limited to a small set of attack types and magnitudes. When the poison-generating algorithms are applied to the popular SWaT dataset, we show that the autoencoder detector trained on the physical system state data is resilient to poisoning in the face of all ten of the relevant attacks in the dataset. This finding suggests that neural network-based attack detectors used in the cyber-physical domain are more robust to poisoning than in other problem domains, such as malware detection and image processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge